Abdominal pain is a common experience. Pain on the left side of the abdomen often causes concern. Many possible reasons exist for left-sided abdominal pain. These range from minor issues to serious medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes empowers individuals. They can then make informed decisions about their health. This blog provides a clear explanation of left-sided abdominal pain. Think of it as an abdominal pain chart. It helps readers navigate this symptom.
Key Takeaways
Many organs are in your left abdomen. Knowing their location helps understand where pain comes from.
Common causes of left-sided abdominal pain include digestive issues like constipation or IBS. Muscle strains can also cause this pain.
Some left-sided abdominal pain needs quick medical help. This includes conditions like diverticulitis or severe IBD.
Watch for “red flag” symptoms. These include very bad pain, vomiting blood, or a high fever. Get medical help right away if you have them.
Left Abdomen: Key Organs
Understanding the organs in the left abdomen helps pinpoint pain sources. The abdomen divides into four main sections. The left side contains many important body parts. Knowing their location helps understand why pain might occur there.
Upper Left Quadrant
The upper left quadrant of the left abdomen holds several vital organs. Pain in this area can come from any of these structures.
Stomach: This organ digests food.
Spleen: It filters blood and supports the immune system.
Left lobe of liver: A small part of the liver extends into this area.
Body of pancreas: This gland produces digestive enzymes and hormones.
Left kidney and adrenal gland: These organs filter waste and produce hormones.
Splenic flexure of colon: This is a bend in the large intestine.
Parts of transverse and descending colon: These are sections of the large intestine.
Pain in the upper left abdomen can relate to these structures.
Lower Left Quadrant
The lower left quadrant of the left abdomen also houses important parts of the digestive and reproductive systems.
Descending colon: This part of the large intestine carries waste downwards.
Sigmoid colon: This S-shaped section connects to the rectum.
Left ureter: This tube carries urine from the left kidney to the bladder.
Left ovary and fallopian tube: These are present in females. They are part of the reproductive system.
Part of the bladder: This organ stores urine.
Pain in the lower left abdomen often points to issues with these organs. Knowing the layout of the left abdomen is crucial for understanding pain.
Common Causes of Left Abdominal Pain

Many reasons exist for left-sided abdominal pain. Some causes are less severe. They are also more common. Understanding these reasons helps people know when to seek medical advice.
Digestive Discomforts
Digestive issues often cause pain in the left abdomen. These problems are usually not serious. They can still cause significant discomfort.
Gastritis: This condition involves inflammation of the stomach lining. It can cause abdominal discomfort in the center or left side of the upper abdomen. This pain often occurs under the ribs. Upper abdominal pain is the main symptom of gastritis. People can feel this pain in the left upper portion of the abdomen. The pain is often sharp and sudden.
Constipation: Difficulty passing stool can lead to left-sided abdominal pain. This pain can be cramping. Some people feel sharp lower left abdominal pain. Other symptoms include hard, dry stools. People may strain to have a bowel movement. They might also feel unable to empty their bowels completely.
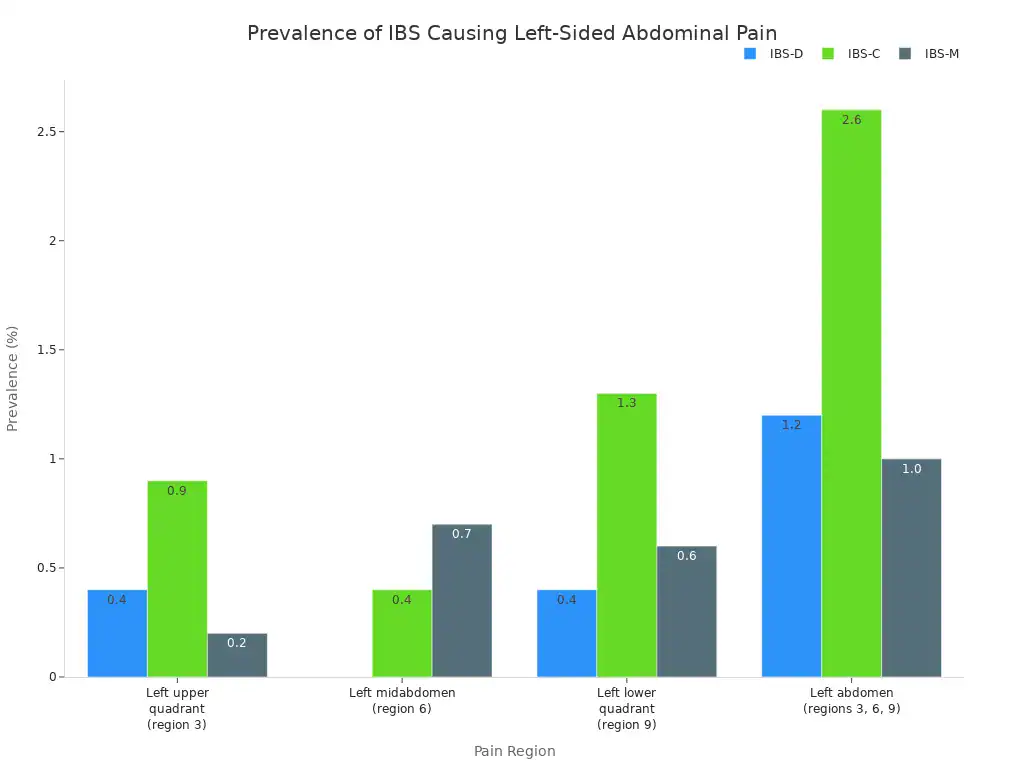
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a common disorder. It affects the large intestine. Symptoms include cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits. The pain can occur on the left side. The table below shows how often IBS causes left-sided abdominal pain in different types of IBS.
Pain Region | IBS-D (n=245) | IBS-C (n=232) | IBS-M (n=681) |
|---|---|---|---|
Left upper quadrant | 0.4% | 0.9% | 0.2% |
Left midabdomen | 0.0% | 0.4% | 0.7% |
Left lower quadrant | 0.4% | 1.3% | 0.6% |
Left abdomen (all regions) | 1.2% | 2.6% | 1.0% |
The chart below visually represents this data.
Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can cause inflammation in the digestive tract. Mild forms can lead to abdominal pain. This pain can occur on the left side.
General Indigestion: Eating too quickly or eating certain foods can cause indigestion. This leads to gas and bloating. These symptoms can result in general abdominal discomfort. This discomfort sometimes localizes to the left side.
Musculoskeletal and Minor Issues
Sometimes, pain in the left abdomen does not come from internal organs. It can come from muscles, bones, or nerves.
Muscle Strain: People can strain muscles in their abdominal wall. This happens during exercise or heavy lifting. Muscle strains cause localized pain. This pain worsens with movement. Injuries to the abdominal wall also cause this type of pain.
Nerve Impingement: Nerves in the abdominal wall can become trapped or irritated. This causes pain. Abdominal Cutaneous Nerve Entrapment Syndrome (ACNES) is a common cause of abdominal pain. It often affects only one side, including the left. The pain is typically well localized. The most common cause of abdominal wall pain is nerve entrapment. This happens at the lateral border of the rectus muscle. Several factors can cause nerve impingement:
Localized compression of the nerve. This happens when a nerve bundle herniates from increased pressure behind the abdominal wall.
Traction on the nerve bundle. This causes it to “strum” against a fibrous ring.
Use of abdominal muscles. This can make nerve impingement worse.
Enlargement of the abdomen. This leads to greater nerve traction.
Scar or suture around the nerve. This directly compresses it or puts it under more traction.
Lateral bending and twisting of the trunk. These movements affect lateral nerve branches.
Bending, lifting, and twisting. These actions affect posterior nerve branches.
Rib Dysfunction/Slipping Rib Syndrome: Problems with the ribs can cause pain. This pain can radiate to the upper left abdomen.
Thoracic Spine Problems: Issues with the mid-back spine can refer pain to the abdomen.
Fascia Problems: The fascia is connective tissue. Problems with this tissue can cause pain.
Psoas Muscle Group Issues: The psoas muscles are deep in the abdomen. Problems with these muscles can cause pain.
Women’s Health and Urinary Issues
Specific conditions related to women’s reproductive health or the urinary system can cause left-sided abdominal pain.
Women’s Health Issues: Several gynecological conditions cause left lower quadrant pain in women.
Menstrual cramps: These are common during a woman’s period.
Ovarian cysts: These are fluid-filled sacs on an ovary. They can cause pain if they grow large or rupture.
Endometriosis: Tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. This causes chronic pain.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This is an infection of a woman’s reproductive organs. It causes pain and other symptoms.
Uterine fibroids: These are non-cancerous growths in the uterus. They can cause discomfort or enlargement of the uterus.
More serious conditions like ectopic pregnancy (a life-threatening pregnancy outside the uterus) or ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary) also cause severe left-sided abdominal pain. These require immediate medical attention.
Kidney Stones: Kidney stones can cause severe left-sided abdominal pain. The pain often begins in the flank area. This is on either side of the middle back. The pain can then move and radiate to the abdomen and groin area. This intense pain can also trigger other symptoms. These include nausea and vomiting. This happens due to a shared nerve connection between the kidneys and the gastrointestinal tract. The pain can occur in the lower back, right/left flank, or groin. It can be severe. Changing positions might not relieve it. The pain can be intermittent or ongoing. People describe it as waves, stabbing, or throbbing. Visible blood in the urine (hematuria) indicates a stone moving from the kidney to the bladder. It might be lodged in the ureter.
Serious Left-Sided Abdominal Pain: When to Seek Help
Some causes of left-sided abdominal pain require immediate medical attention. Other conditions are chronic. They need ongoing management. Recognizing the difference helps people make informed health decisions.
Urgent Medical Conditions
Certain conditions causing left-sided abdominal pain are medical emergencies. They need prompt evaluation and treatment.
Diverticulitis: This condition involves inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) in the digestive tract. These pouches often form in the sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon is on the lower left side of the abdomen. Therefore, diverticulitis pain typically occurs in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen. This lower abdominal pain can sometimes spread to the pelvis or radiate to the back. People often experience several symptoms with diverticulitis.
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom. It often feels like a sudden, severe pain in the lower left side. Movement or eating can make it worse.
Changes in bowel habits may occur. These include constipation or diarrhea. People might also feel like they cannot fully empty their bowels.
A mild to moderate fever can develop. This sometimes comes with chills or night sweats. It signals infection or inflammation.
Nausea and vomiting can happen. This is especially true with worsening inflammation or infection. It can make eating difficult.
Bloating and gas are common. People often feel full and tender in the abdomen.
Rectal bleeding is less common. It can show bleeding from inflamed diverticula. When experiencing stomach pain, noting its location is crucial. Lower left-side pain could indicate diverticulitis. This condition may require immediate medical attention depending on its severity.
Colitis: This is inflammation of the colon. It can cause significant left-sided abdominal pain. Ulcerative colitis, a type of IBD, often affects the left side of the colon. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and urgency.
Splenomegaly: This means an enlarged spleen. The spleen sits in the upper left abdomen. An enlarged spleen can cause discomfort or pain under the left ribs. It can also cause early satiety. This means a person feels full after eating only a small amount. This happens because the enlarged spleen presses on the stomach.
Other Acute Conditions: Other urgent issues can cause severe abdominal pain. These include a ruptured ectopic pregnancy in women. This is a life-threatening condition. Ovarian torsion, where an ovary twists, also causes sudden, severe pain. A ruptured aortic aneurysm is another critical condition. It causes sudden, intense abdominal pain.
Chronic Conditions
Some serious conditions cause ongoing or recurring left-sided abdominal pain. They require long-term medical management.
Chronic Pancreatitis: This is long-lasting inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is in the upper abdomen. Chronic pancreatitis can cause persistent or recurring left-sided abdominal pain. This pain often radiates to the back. It can worsen after eating. Chronic pancreatitis can lead to several long-term complications.
Chronic debilitating pain is a common issue.
Diabetes can develop.
Pancreatic pseudocysts may form. These can rupture, become infected, bleed, or cause obstructions.
Pancreatic cancer is a risk.
Osteoporosis or osteopenia can occur.
Pancreatic abscesses and necrosis can result from recurrent acute attacks.
Sepsis and multi-organ failure are possible from recurrent acute attacks.
Severe Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): While mild IBD was mentioned earlier, severe cases of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can cause intense and chronic left-sided abdominal pain. These conditions require aggressive treatment to manage inflammation and prevent complications.
Red Flag Symptoms
Certain symptoms, when present with left-sided abdominal pain, signal a medical emergency. People should seek immediate medical help if they experience these “red flag” symptoms.
Severe and Sudden Pain: Excruciating or unbearable abdominal pain with an abrupt onset needs urgent attention. This can point to conditions like peptic ulcers, ruptured aortic aneurysms, or pancreatitis.
Persistent Pain: Abdominal pain lasting several hours or days without improvement is concerning. It could signal issues such as pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, or a gastrointestinal blockage.
Pain Accompanied by Vomiting Blood (Hematemesis): This is a medical emergency. It can point to severe conditions like bleeding ulcers, esophageal varices, or other gastrointestinal bleeding.
Blood in Stool: Fresh blood or tarry-black stools are warning signs. They indicate various gastrointestinal conditions. These include bleeding ulcers, colorectal cancer, or inflammatory bowel disease.
High Fever and Chills: These suggest an underlying infection or inflammation inside the abdominal cavity. This could be due to pancreatitis, peritonitis, or abscesses.
Inability to Pass Gas or Have a Bowel Movement: This, along with abdominal pain, may indicate a life-threatening intestinal obstruction.
Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes (Jaundice): This is a sign of liver or bile duct issues. It could result from gallstones, hepatitis, or liver cirrhosis.
Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy: Severe abdominal pain in pregnant individuals requires immediate medical attention. It can signal potential complications like ectopic pregnancy or preeclampsia.
Severe Back or Shoulder Pain: Abdominal pain radiating to the back or shoulder blades may indicate pancreatitis, gastric ulcers, or cholecystitis.
New Onset of Pain in Older Adults: Gastric pain that is new or has changed in character in older adults can be a sign of serious conditions. These include colorectal cancer or diverticulitis.
This abdominal pain chart helps identify potential issues. However, it does not replace professional medical advice.
Left-sided abdominal pain can stem from many causes, ranging from harmless to serious. This abdominal pain chart provides valuable information. However, it is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis. If you experience persistent, severe, or concerning left-sided abdominal pain, especially with red flag symptoms, seek prompt medical evaluation. Proactively manage your health and communicate openly with healthcare providers.
FAQ
What is the difference between upper and lower left abdominal pain?
Pain in the upper left abdomen often relates to organs like the stomach, spleen, or pancreas. Pain in the lower left abdomen usually involves the descending colon, sigmoid colon, or left ovary in females. The location helps doctors identify the source.
What are “red flag symptoms” for left abdominal pain?
“Red flag symptoms” are signs of a serious medical problem. They include severe, sudden pain, vomiting blood, or blood in stool. High fever, chills, or jaundice are also red flags. Seek immediate medical help with these symptoms.
What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is inflammation or infection of small pouches in the digestive tract. These pouches are called diverticula. It often causes pain in the lower left abdomen. Other symptoms include fever and changes in bowel habits.
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
IBS is a common disorder affecting the large intestine. It causes symptoms like cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, and gas. People with IBS also experience changes in bowel habits. The pain can occur on the left side.