
You know the feeling: muffled hearing, a sense of fullness, and persistent ear pressure. These are common signs of a clogged Eustachian tube, often accompanied by popping sounds or even mild dizziness. When your ears feel blocked, you want quick relief.
This post gives you five fast, effective, and safe solutions to help you unclog eustachian tube and relieve ear pressure. Remember, these are home remedies for temporary comfort; they do not replace professional medical advice for ongoing issues or severe pain.
Key Takeaways
Your Eustachian tube balances ear pressure. It connects your middle ear to your throat. Blockages cause muffled hearing and ear pressure.
You can try simple actions to clear your ears. Yawning, swallowing, and chewing gum help open the tube. The Valsalva maneuver also helps, but use it gently.
Nasal sprays and decongestants reduce swelling. They help your Eustachian tubes open. A warm compress can also ease discomfort and loosen mucus.
See a doctor if ear symptoms last over two weeks. Also seek help for severe pain, ear discharge, or hearing loss. Children need quicker medical attention for ear issues.

What is a Eustachian Tube
You have a small but important structure in your head called the Eustachian tube. Also known as the auditory or pharyngotympanic tube, it connects your middle ear to your nasopharynx. This tube is made of both bone and fibrocartilage.
It starts from the front wall of your middle ear and extends downwards, forwards, and towards the middle of your head to reach the nasopharynx. You have a tympanic opening into the middle ear and a pharyngeal opening into the nasopharynx. The tube has a bony part closer to your middle ear and a cartilaginous part closer to your nasopharynx.
The main job of your Eustachian tube is to balance the air pressure inside your middle ear with the air pressure outside. This equalization happens when the tube opens. Muscles like the tensor veli palatini and levator veli palatini in your soft palate help it open when you swallow.
The tensor veli palatini is especially important for active opening. Your Eustachian tube also helps clear mucus from your middle ear into your nasopharynx. It protects your middle ear from germs and sounds coming from your nasopharynx. This tube also plays a role in how you hear sound waves.
Common Causes of Blockage
When your Eustachian tube does not work correctly, you experience eustachian tube dysfunction. This condition, often called ETD, leads to those uncomfortable blocked ears. Several factors can cause ETD.
One common reason for ETD is a functional obstruction. This happens when your Eustachian tube lacks stiffness or your tensor veli palatini muscle does not work efficiently. This muscle is vital for opening the tube.
You can also experience mechanical obstruction. This means something physically blocks the tube. Extrinsic factors, like tumors in your nasopharynx or enlarged adenoids, can cause this. Intrinsic factors, mainly from upper respiratory tract infections, also lead to mechanical blockage.
Inflammation is another major cause of ETD. Upper respiratory allergies can cause partial obstruction of your Eustachian tube. Allergic reactions make your mast cells and inflammatory cells release chemicals.
These chemicals cause swelling and block the tube. Chronic acidic reflux, known as laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), also causes inflammation. Acid exposure irritates the lining around the Eustachian tube openings in your throat. This swelling narrows the tubes, stopping proper airflow and fluid drainage. This makes it hard for the tubes to open and close correctly. This swelling traps air pressure and fluid in your middle ear, contributing to blockage.
Colds and sinus infections are frequent causes of eustachian tube dysfunction. A study showed that ear symptoms during a cold or sinusitis are very common with ETD. Environmental irritants like smoke or pollution also cause inflammation and restrict airflow. These are all common causes of eustachian tube dysfunction.
Quick Solutions to Unclog Eustachian Tube
You can take several actionable steps at home to relieve ear pressure. These methods help to open your Eustachian tubes and restore comfort.
The Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is a common technique to equalize pressure in your ears. You close your mouth and pinch your nose shut. Then, you gently blow air out as if you are blowing your nose. This action creates pressure in your nasal cavity. This pressure helps to open your Eustachian tubes.
It equalizes the pressure across your eardrum. This maneuver generates about 20–40 mm of Hg pressure. This pressure helps to unclog eustachian tube.
When ambient pressure increases quickly, like during a plane descent, your Eustachian tubes tend to stay closed. This causes painful pressure differences. The Valsalva maneuver can open these tubes if other methods do not work. However, using this maneuver too forcefully can damage your ear. It can over-pressurize your middle ear. Safer options like swallowing or yawning are better if you have enough time.
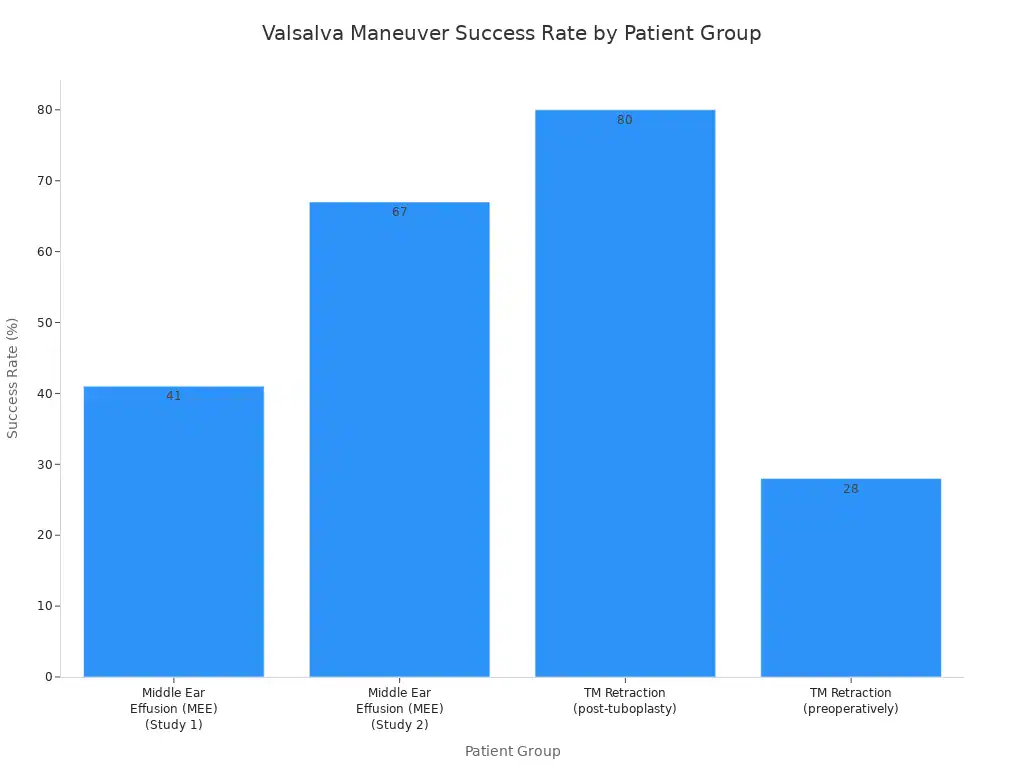
The success rate of the Valsalva maneuver varies. It depends on your specific ear condition.
Patient Group | Valsalva Success Rate |
|---|---|
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE) | 41% (at 6-month follow-up in one study) |
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE) | 67% (in another study) |
TM Retraction (post-tuboplasty) | 80% |
TM Retraction (preoperatively) | 28% |
In healthy people, the Valsalva maneuver helps equalize middle ear pressure about 51.7% of the time.
Yawning and Swallowing
Yawning and swallowing are simple, effective ways to open your Eustachian tubes. Your Eustachian tube normally opens each time you swallow or yawn. This action works like a pressure-equalizing valve for your middle ear. These self-care measures help equalize ear pressure. They are especially helpful during altitude changes, such as when you fly or drive through mountains. They keep your Eustachian tubes open and working correctly.
Yawning helps to open your Eustachian tubes.
Swallowing activates the muscles that open your Eustachian tube. Sipping water or sucking on hard candy increases your need to swallow. This further helps the process.
Chewing Gum or Sucking Candy
Chewing gum or sucking on hard candy also helps to unclog eustachian tube. This action stimulates your swallowing reflex. When you swallow, muscles automatically open your Eustachian tube. This tube connects your middle ear to the back of your nose.
This opening allows for pressure equalization in your middle ear. You often feel a “popping” sensation. Chewing gum or sucking on hard candy helps activate this response. This method is very effective during air travel or when you experience altitude changes.
Nasal Sprays and Decongestants
Nasal sprays and decongestants can reduce inflammation and swelling in your nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. This helps them open more easily.
Saline Nasal Spray: This spray is good for congestion or stopped-up ears. It has almost no side effects. It does not cause rebound congestion or tolerance build-up.
Topical Steroid Sprays: These sprays work directly on your nasal lining. They avoid whole-body side effects. Flonase, with its active ingredient fluticasone propionate, is a corticosteroid nasal spray. It reduces inflammation in your nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. It targets the inflammation that causes tube swelling and blockage. This allows your tubes to open better and work normally. It helps with pressure equalization and fluid drainage. Nasacort (triamcinolone) is another example. These are some of the best decongestants for long-term use.
Topical Decongestant Sprays: These sprays give immediate relief for severe congestion. Afrin (oxymetazoline) and 4-Way (phenylephrine nasal) are examples. You should use these for only about three days at a time. Overuse can cause severe rebound congestion. These are also among the best decongestants for quick relief.
Oral Decongestants: These medications, like pseudoephedrine, can also reduce inflammation. They are some of the best decongestants for systemic relief. However, they can cause side effects. These include nervousness and insomnia. They have effects similar to epinephrine and amphetamines. You should use them with caution. They are not for people taking MAO inhibitors. Use them carefully if you have high blood pressure or an enlarged prostate. These are some of the best decongestants but require careful consideration of your health.
These options help to alleviate eustachian tube dysfunction by reducing swelling.
Warm Compress Application
Applying a warm compress can help loosen mucus and reduce discomfort. The warmth can soothe discomfort and encourage fluid drainage. It helps reduce congestion and promotes the opening of your Eustachian tubes.
To apply a warm compress:
Pour hot water onto a clean washcloth.
Squeeze out any excess water from the soaked cloth.
Hold the warm, damp washcloth below your affected ear for about 5 to 10 minutes.
A warm compress increases blood flow to your ear. This helps loosen fluid. It also helps reduce pain and inflammation. You can apply a warm, moist washcloth against your affected ear for 10-15 minutes. This provides comfort and helps reduce pain. Alternating between warm and cool compresses may further help with pain relief.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
While home remedies offer quick relief, you must know when to seek professional medical help. Certain signs indicate a more serious issue with your Eustachian tubes.
Persistent Symptoms
You should consult a doctor if your ear symptoms do not improve. If you experience symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction for more than two weeks, you need a medical evaluation. This includes ongoing muffled hearing, fullness, or pressure. Do not delay seeking medical attention if your etd symptoms last longer than two weeks or frequently recur. Persistent etd can lead to other problems.
Severe Pain or Discharge
You must see a doctor immediately if you experience severe ear pain. Any discharge from your ear, such as pus or blood, is a serious warning sign. These symptoms suggest a possible infection or eardrum damage. They require prompt medical attention. Ignoring these signs can lead to worse conditions.
Hearing Loss or Dizziness
If you notice sudden or worsening hearing loss, you should contact a healthcare professional. Persistent dizziness or vertigo also warrants a medical visit. These symptoms can indicate significant issues with your middle ear or inner ear. They need proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms in Children
Children often face a higher risk for etd. Their Eustachian tubes are shorter and flatter. This makes them more prone to blockages. If your child shows signs of eustachian tube dysfunction, you should seek medical advice sooner. Untreated etd in children can lead to persistent ear infections, hearing loss, and eardrum damage. This significantly impacts their quality of life.
For persistent etd in children, medical treatments vary. Doctors often recommend non-surgical options for mild cases. These include nasal sprays or decongestants. However, no medications have shown long-term benefits for etd in children. Oral corticosteroids offer only short-term improvement.
Nasal corticosteroids do not resolve middle ear fluid or improve hearing. Decongestants and antihistamines also lack significant improvement. They can cause side effects like irritability. For chronic etd, surgical options are often effective. Myringotomy and ear tube insertion provide long-term relief. Ear tubes prevent fluid buildup and regulate ear pressure. The Hummingbird Ear Tube System offers a minimally invasive alternative. It provides quicker recovery and improved comfort for children.
You now have five simple, effective solutions to help you unclog eustachian tube and relieve ear pressure. Remember the Valsalva maneuver, yawning, chewing gum, using nasal sprays, and applying a warm compress.
These methods offer quick, temporary relief. However, you must listen to your body. If symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional. Untreated, long-term eustachian tube dysfunction can cause significant damage to your eardrum and middle ear, including hearing loss or severe ear infections. To prevent future blockages, manage your allergies and avoid irritants like tobacco smoke. Keep your ears clean and dry.
FAQ
What is a clogged Eustachian tube?
A clogged Eustachian tube means your middle ear cannot equalize pressure with the outside air. This tube connects your middle ear to your throat. When it blocks, you feel ear fullness, muffled hearing, or pressure. It stops working correctly.
What causes Eustachian tube blockage?
Many things cause blockages. Colds, allergies, and sinus infections often lead to inflammation. This swelling narrows the tube. Altitude changes, like flying or driving in mountains, also create pressure differences. These factors stop your tube from opening.
What happens if I do not unclog my Eustachian tube?
Leaving your Eustachian tube clogged can cause problems. You might get ear infections. It can also lead to fluid buildup in your middle ear. This can cause pain, hearing loss, or even damage your eardrum over time.
What can I do to prevent clogged Eustachian tubes?
You can take steps to prevent blockages. Manage your allergies with medication. Avoid irritants like smoke. When flying, chew gum or swallow often. This helps your Eustachian tubes open. Stay hydrated to keep mucus thin.




