Experiencing Shortness Of Breath While Talking is a critical symptom. This issue often signals serious, life-threatening conditions. It acts as a vital red flag for health emergencies. People must recognize these urgent signs. They should never delay seeking immediate medical help. Shortness of breath accounts for a significant portion of emergency room visits. Studies show it contributes to 2.7% to 9% of all emergency department presentations. Immediate medical evaluation for Shortness Of Breath While Talking is crucial.
Key Takeaways
Shortness of breath while talking is a serious sign. It often means a health emergency. You must get medical help right away.
Look for other serious signs with shortness of breath. These include chest pain, blue lips, or confusion. These mean you need emergency care.
Heart problems like a heart attack or lung issues like severe asthma can cause this. They make it hard for your body to get enough oxygen.
If you or someone else has urgent shortness of breath, call 911 immediately. Give clear information. Do not wait to get help.
Recognizing Urgent Shortness of Breath While Talking
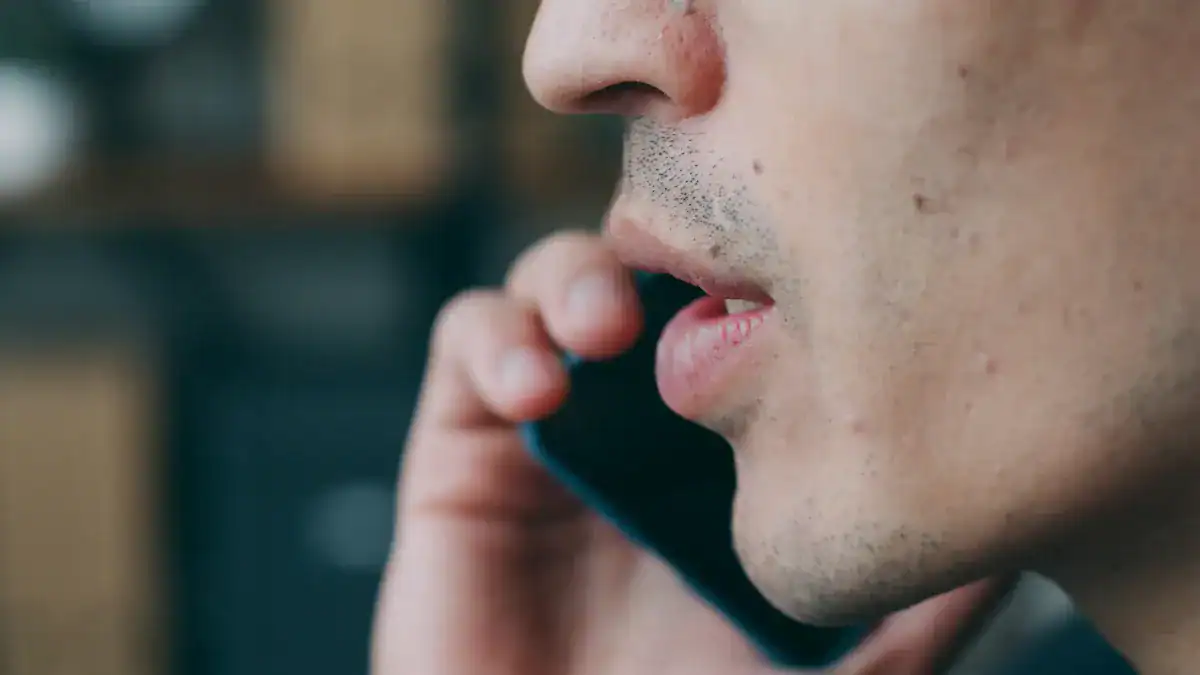

Defining Urgent Symptoms
Not all instances of breathlessness signal an emergency. However, certain accompanying symptoms turn shortness of breath into a critical medical situation. Individuals must recognize these warning signs. They indicate a need for immediate medical evaluation. When someone experiences Shortness Of Breath While Talking along with other severe signs, they face a serious health risk.
Here are specific symptoms that signal a medical emergency:
Sudden and serious breathing trouble that does not improve with rest.
Chest discomfort or pain.
Inhaling food or an object affects breathing.
Blue or gray tint to lips or nails.
Feeling faint or nauseated.
Confusion or drowsiness.
Coughing up blood.
Fever or chills.
Inability to sleep or perform activities due to breathing difficulties.
Heart beats much faster than usual.
Why Immediate Medical Help is Crucial
Delaying medical help in these situations can have severe consequences. Many conditions causing urgent shortness of breath progress quickly. For example, a heart attack or a severe asthma attack can worsen rapidly.
Timely intervention can prevent permanent damage or even save a life. Medical professionals can diagnose the underlying cause quickly. They then provide the necessary treatment. Waiting can lead to more complex health problems. It also reduces the chances of a full recovery. Therefore, individuals must seek emergency care without hesitation when these urgent symptoms appear.
Cardiovascular Causes of Shortness of Breath
Several heart conditions can cause urgent shortness of breath. These conditions affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. This leads to problems with oxygen delivery throughout the body. When the body does not get enough oxygen, breathing becomes difficult. Talking also becomes a challenge.
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
A heart attack happens when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle stops. This usually occurs because a blood clot blocks a coronary artery. Without blood, the heart muscle begins to die. This damage makes the heart unable to pump blood efficiently. The body then struggles to get enough oxygen.
This causes severe shortness of breath. The effort of speaking increases the body’s oxygen demand. An impaired heart cannot meet this demand. This leads to breathlessness, especially when someone experiences Shortness Of Breath While Talking.
Chest pain is a primary symptom of a heart attack. Doctors categorize chest pain as cardiac, possible cardiac, or non-cardiac. Cardiac pain clearly comes from the heart or a blocked blood vessel. Possible cardiac pain has an unclear heart-related origin.
Non-cardiac pain is not from the heart. An advanced blood test, high-sensitivity troponin, quickly determines if someone has a heart attack. Doctors diagnose a heart attack by detecting a rise or fall of cardiac troponin values. These values must be above the 99th percentile of the normal range.
Other signs include symptoms of ischemia, new ECG changes (like ST segment T wave changes or left bundle branch block), development of pathologic Q waves, imaging evidence of new heart muscle loss, or identification of an intracoronary thrombus. For STEMI, specific ST segment elevation criteria apply to different leads.
A new left bundle branch block with chest pain and elevated troponin also indicates a heart attack. Doctors perform a 12-lead electrocardiography within 10 minutes of presentation. They also assess risk using history and physical examination. Cardiac troponin measurements occur at presentation and three to six hours after symptom onset.
Heart Failure Exacerbation
Heart failure means the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. An exacerbation is a sudden worsening of this condition. When heart failure worsens, the heart struggles even more to pump blood.
This causes fluid to build up in the lungs. This fluid is called pulmonary edema. It makes it very hard for oxygen to enter the bloodstream. The increased effort to breathe due to fluid in the lungs makes speaking difficult. People often experience difficulty speaking in complete sentences due to shortness of breath.
Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs. This clot blocks blood flow in one or more arteries in the lungs. The blockage prevents blood from reaching parts of the lung.
This stops oxygen from entering the blood effectively. The body cannot get enough oxygen. This leads to compromised oxygen exchange. Any physical exertion, including talking, becomes very difficult. This causes significant breathlessness.
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiac tamponade is a serious condition. Fluid builds up in the sac around the heart. This fluid compresses the heart. The compression prevents the heart from filling properly with blood.
It also stops the heart from pumping enough blood to the body. The heart’s reduced pumping ability leads to low oxygen delivery. This causes breathlessness, especially with exertion like talking.
Respiratory Emergencies Affecting Speech
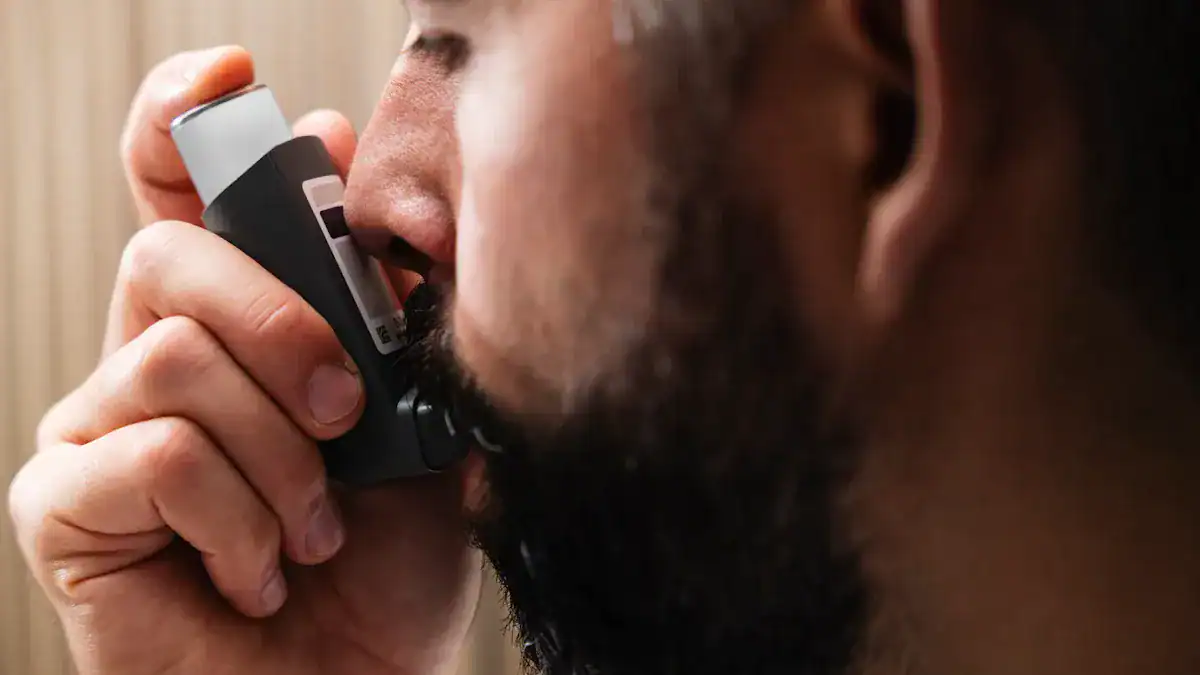

Respiratory emergencies directly disrupt lung and airway function. When breathing becomes difficult, speaking becomes equally challenging. Because the body struggles to take in enough oxygen, even minimal vocal effort can lead to breathlessness.
Severe Asthma Attack
During a severe asthma attack, the airways become significantly narrowed. The surrounding muscles tighten, the airway lining swells, and mucus production increases. Together, these changes obstruct airflow and make breathing extremely difficult. People often experience wheezing, coughing, and marked shortness of breath. Speaking requires additional oxygen, which the constricted airways cannot supply, resulting in pronounced difficulty talking.
Severe asthma can lead to dangerously low blood oxygen levels. An oxygen saturation level below 92% is considered clinically severe and requires close monitoring. Supplemental oxygen is often needed when levels drop below this threshold, with the goal of maintaining at least 90% saturation. Research shows that respiratory failure is highly unlikely when oxygen saturation is 92% or higher, while lower levels indicate significantly higher risk.
| Oxygen Saturation Level | Patients with Respiratory Failure |
|---|---|
| 92% or higher | 1.13% |
| 90% to 92% | 28% |
| Less than 90% | 60% |
COPD Exacerbation
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) gradually limits airflow, making breathing harder over time. A COPD exacerbation is a sudden worsening of symptoms, marked by increased breathlessness, coughing, and mucus production. Inflammation increases, further narrowing the airways and impairing oxygen–carbon dioxide exchange. Even simple tasks—such as speaking—become exhausting.
Common triggers of COPD exacerbations include:
- Respiratory infections (cold, flu, pneumonia, COVID-19, sinus infections)
- Secondhand smoke exposure
- Air pollution (vehicle exhaust, gas fumes, fireplace or cooking smoke, poor outdoor air quality)
- Strong odors, chemicals, dust, and fumes (perfumes, cleaning products, scented candles, occupational exposures)
- Extreme temperatures (high humidity, very cold or hot weather)
- Allergens (pet dander, pollen, mold, dust)
- Other medical conditions (e.g., congestive heart failure, pulmonary embolism)
Severe Pneumonia
Severe pneumonia is a major lung infection that causes widespread inflammation in the air sacs (alveoli). These sacs fill with fluid or pus, making oxygen transfer into the bloodstream extremely difficult. The body must work harder to breathe, leading to profound shortness of breath. Speaking becomes increasingly difficult due to the high respiratory effort required.
Severe pneumonia can also affect vocal function. Many survivors—especially those recovering from COVID-19—report voice problems such as phonasthenia (vocal fatigue), dysphonia (hoarseness), and reduced maximum phonation time (MPT), which measures how long a person can sustain a vowel sound on one breath. A shorter MPT indicates reduced lung volume and impaired vocal capacity.
Key findings include:
- Severe pneumonia significantly impairs phonatory function, causing voice weakness and hoarseness.
- Reduced lung function—such as lower vital capacity—directly affects voice quality and MPT.
- Severe pneumonia survivors show higher rates of voice weakness (87.5%) compared with less severe cases (60.8%) and healthy individuals.
- Average MPT is drastically reduced in severe pneumonia survivors (8.88 seconds), indicating marked respiratory and vocal impairment.
- These voice issues stem from reduced lung volume, fatigue, shortness of breath, overall weakness, and possible laryngeal irritation from coughing.
Efficient breath control is essential for normal speech. When respiratory strength is compromised, vocal patterns and the ability to sustain sound are affected.
Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)
A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between the lung and chest wall, causing the lung to collapse. This prevents the lung from fully expanding and significantly limits oxygen intake. The condition leads to sudden, sharp chest pain and severe shortness of breath. Because the body cannot obtain adequate oxygen, any attempt to speak becomes extremely difficult and painful.
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm is a sudden tightening of the muscles surrounding the airways. This constriction narrows the airways and restricts airflow. Bronchospasm may result from asthma, allergies, or exposure to irritants.
It commonly causes wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. With reduced airflow, oxygen intake decreases, leading to breathlessness. Because speaking requires controlled exhalation, bronchospasm disrupts this process, making speech strained and challenging.
Other Urgent Causes of Breathlessness
Several other conditions can cause sudden and severe breathlessness. These situations demand immediate medical attention. They can quickly become life-threatening.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. The body releases too many histamines in response to an allergen. Histamine causes swelling. This swelling can lead to difficulty breathing.
Common allergens include foods like peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, and shellfish. Insect stings from bees, wasps, and fire ants also trigger reactions. Certain medications, latex, and animal dander can also cause anaphylaxis. Individuals with asthma are more susceptible. Both conditions affect the airways.
Foreign Body Aspiration
Foreign body aspiration happens when an object enters the airway. This can cause choking or difficulty breathing.
The object may lodge in the trachea or a bronchus. Symptoms depend on the object’s size, nature, and location. Immediate signs include choking, coughing, and difficulty breathing. People may also have trouble speaking. A bluish tint to the skin can appear. Severe obstructions prevent breathing or speaking.
Sudden Airway Blockage
A sudden airway blockage occurs when something completely obstructs the breathing passage. This is a medical emergency. The most common causes in adults are food items.
Meat products, such as fish or sausages, account for a large percentage of cases. Breads, fruits, and vegetables are also frequently involved. This blockage prevents air from reaching the lungs.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning severely impairs oxygen delivery. CO binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells. It has a much stronger affinity for hemoglobin than oxygen. This forms carboxyhemoglobin.
This process prevents oxygen from reaching vital organs, especially the brain. The blood’s ability to carry and release oxygen drastically reduces. This leads to tissue hypoxia. Brain damage can occur from this oxygen deprivation.
Severe Anxiety or Panic Attack
Severe anxiety or a panic attack can cause intense breathlessness. These attacks are not physically life-threatening. However, their symptoms can mimic urgent physical conditions. People may experience a sudden feeling of suffocation. They might hyperventilate.
This rapid breathing can lead to dizziness, tremors, and palpitations. The brain’s fear network becomes oversensitive. This creates a “false suffocation alarm.” This can make individuals feel like they cannot breathe or speak, similar to experiencing Shortness Of Breath While Talking from a physical cause. Immediate management helps calm the person and address these distressing symptoms.
What to Do: Urgent Shortness of Breath While Talking
Experiencing urgent shortness of breath while talking requires immediate action. Staying calm is important. You must provide clear, accurate information to emergency services. Low blood pressure can also be an urgent sign.
Call 911 Immediately
Do not hesitate to call 911 if you or someone else experiences urgent shortness of breath. This is a medical emergency. When speaking with 911, remain calm. Being upset can make it difficult for the dispatcher to understand you. This delays critical information. Taking a deep breath and focusing can save valuable time.
Provide specific details to the dispatcher:
The exact address of the emergency. Be ready to repeat it for accuracy.
Your callback number for verification.
Whether the person is conscious.
Whether the person is breathing.
Explicitly state that you are experiencing difficulty breathing now.
Mention any medications the patient takes.
List any known allergies.
Do Not Delay Medical Help
Delaying medical treatment for acute shortness of breath carries significant risks. It can lead to negative patient outcomes. This includes increased illness and death. Increased delay in seeking medical care can make patients ineligible for life-saving treatments.
For example, with acute coronary syndrome, the risk of 1-year mortality increases by 7.5% for every 30 minutes of delay. This diminishes the effectiveness of revascularization procedures. Shortness of breath can signal a heart attack. This serious condition requires prompt attention. Delaying care for serious medical conditions hinders effective treatment.
Provide Clear Information
When emergency responders arrive, give them clear and concise information. Describe the symptoms you observe. Tell them when the symptoms started. Mention any relevant medical history. This helps them quickly understand the situation. It allows them to provide the best possible care. Your clear communication is vital for a quick and accurate diagnosis.
Tip: Write down key information beforehand if possible. This includes medical history, current medications, and allergies. This helps you stay organized during an emergency.
Shortness of breath while talking is a serious symptom. It demands immediate attention, especially with other severe signs. Recognizing these urgent causes can save lives. An inability to speak in full sentences due to breathlessness indicates a need for emergency care. If someone experiences shortness of breath at rest or chest tightness, they need urgent medical attention. Trust your instincts. Seek emergency care without hesitation if you suspect a serious issue. Call 9-1-1 immediately if a person requires emergency medical treatment.




