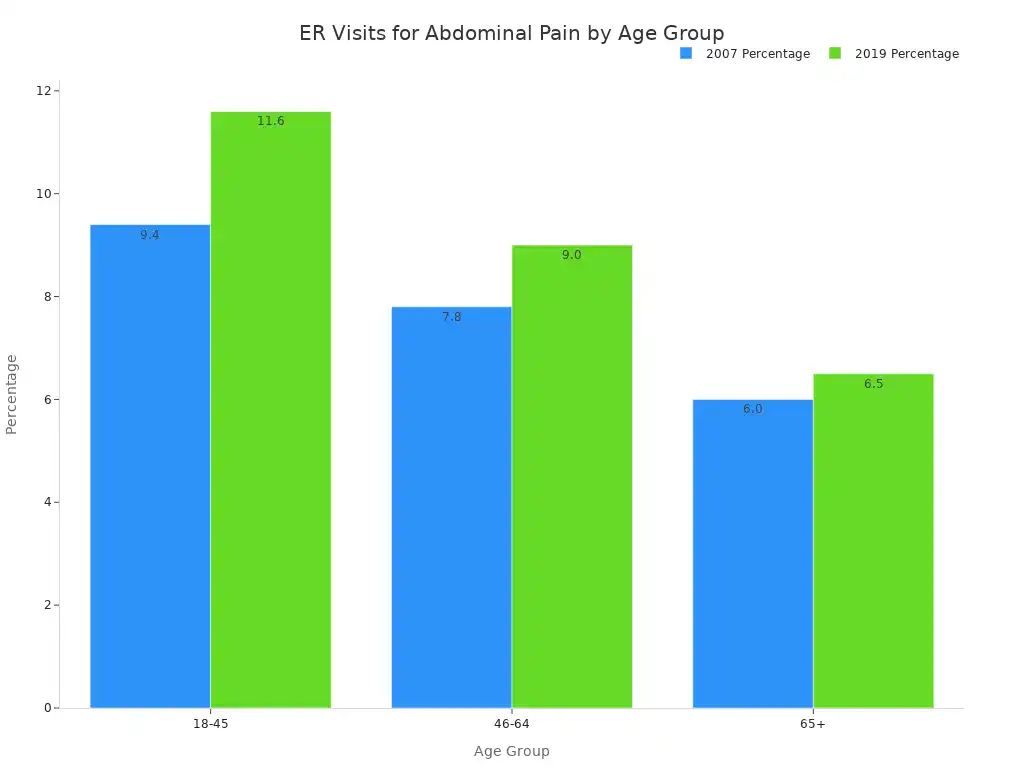
You might experience abdominal pain frequently. However, when you feel pain in your lower left abdomen, it can sometimes signal urgent issues. While many types of abdominal pain are minor, some causes demand immediate medical attention. Abdominal pain accounts for a significant portion of emergency room visits, highlighting its importance.
This blog explains these Urgent Causes Explained. It also guides you on when to seek care for this type of pain in your abdomen.
Key Takeaways
Severe lower left abdominal pain can signal serious health problems. You must know when to get medical help.
Look for ‘red flag’ symptoms like very bad pain, sudden pain, fever, throwing up a lot, or blood in your stool. These mean you need a doctor right away.
Conditions like diverticulitis, ectopic pregnancy, and kidney stones cause urgent lower left abdominal pain. They need quick medical care.
Doctors use questions, exams, and tests like CT scans to find the cause of your pain. This helps them give you the right treatment.
When To Seek Care For Abdominal Pain

Knowing when to seek care for abdominal pain is crucial. While many instances of discomfort pass quickly, certain signs tell you that you need immediate medical attention. You must recognize these warning signs.
Red Flag Symptoms
You should look for specific symptoms that signal a serious problem. These are often called “red flag symptoms.” If you experience any of these, you need to see a doctor right away.
Severe Pain: You have severe pain that makes it difficult to move, eat, or drink. This kind of pain can stop you from doing normal activities.
Sudden Onset: The pain starts very suddenly and intensely. This sudden, severe pain can indicate a serious issue.
Pain That Worsens: Your pain gets worse over time, or it does not ease within 30 minutes. Continuous, severe abdominal pain, especially with continuous vomiting, is a major concern.
Fever: You have a high fever along with your abdominal pain. This can mean your body is fighting an infection.
Vomiting: You experience persistent vomiting. If you are also coughing up or vomiting blood, this is an emergency.
Blood in Stools: You see blood in your stool or experience bloody diarrhea. This is a critical symptom.
Hard Abdomen: Your abdomen feels extremely hard or is painful to touch. This tenderness can point to inflammation or other serious conditions.
Dizziness or Fainting: You feel dizzy or faint. These symptoms can mean you are losing a lot of blood or are in shock.
Difficulty Breathing or Chest Pain: You have trouble breathing or experience chest pain along with your abdominal pain. Pain in the upper abdomen under the rib cage, especially with severe nausea, can sometimes indicate heart problems.
Trouble with Bowel Movements: You have difficulty having a bowel movement, which could suggest a blockage.
Trauma: Your stomach pain follows an accident that caused trauma to your abdomen.
An acute abdomen, characterized by sudden, severe abdominal pain, often signals a medical emergency. This may need urgent treatment, possibly even immediate surgery, even if pain is your only symptom.
Differentiating Urgent From Non-Urgent
You can often tell the difference between urgent and non-urgent abdominal pain by how severe your symptoms are and how quickly they start.
Urgent Pain: This pain is usually sudden, intense, and does not go away. It often comes with other serious symptoms like fever, vomiting, or blood in stools. For example, if you have severe pain in your lower right abdomen, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, or fever, these are symptoms of appendicitis. If you experience severe abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, these are symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy. Pain in the middle upper abdomen that lasts for days, becoming severe and constant, along with nausea, a swollen abdomen, fever, and a rapid pulse, can be symptoms of acute pancreatitis. These conditions require immediate medical attention.
Non-Urgent Discomfort: This pain is usually mild to moderate. It might come and go, or it might improve with home remedies. You might feel some discomfort from gas, indigestion, or mild constipation. These types of pain do not typically come with the red flag symptoms listed above. You might have some mild, painful cramps during your menstrual cycle. While uncomfortable, these are usually not an emergency.
If you are unsure, it is always best to seek medical advice. Trust your instincts. If you feel your pain is severe or unusual, you should contact a healthcare professional.
Urgent Causes Of Lower Left Abdominal Pain
You need to understand the specific conditions that can cause pain in your lower left abdomen. These are severe causes that often require immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms helps you act quickly. This section explains these urgent causes explained.
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis occurs when small pouches, called diverticula, in your colon become inflamed or infected. These pouches often form in the lower part of your large intestine. When they become inflamed, you feel pain in your lower left abdomen.
You typically experience acute, constant abdominal pain in your lower left side. Other symptoms include loss of appetite, constipation, nausea, diarrhea, and painful urination. You might also have a fever, usually below 102°F (39°C). Your doctor will check for tenderness in your lower left abdomen. This tenderness strongly suggests acute diverticulitis. Blood tests often show an increase in white blood cells, present in about 55% of cases. A C-reactive protein (CRP) level above 50 mg/L, combined with lower left quadrant tenderness and no vomiting, increases the likelihood of diverticulitis.
Doctors use computed tomography (CT) scans to diagnose diverticulitis. CT scans accurately show the disease’s extent and severity. They also help rule out complications. Other imaging options include ultrasound, especially for pregnant women, and MRI. These offer good diagnostic accuracy without radiation. You should not have a colonoscopy during acute diverticulitis. Doctors recommend it four to six weeks after your symptoms resolve. This confirms the diagnosis and checks for other conditions.
Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside your uterus. This usually occurs in a fallopian tube. This condition is a medical emergency because it can be life-threatening if the tube ruptures.
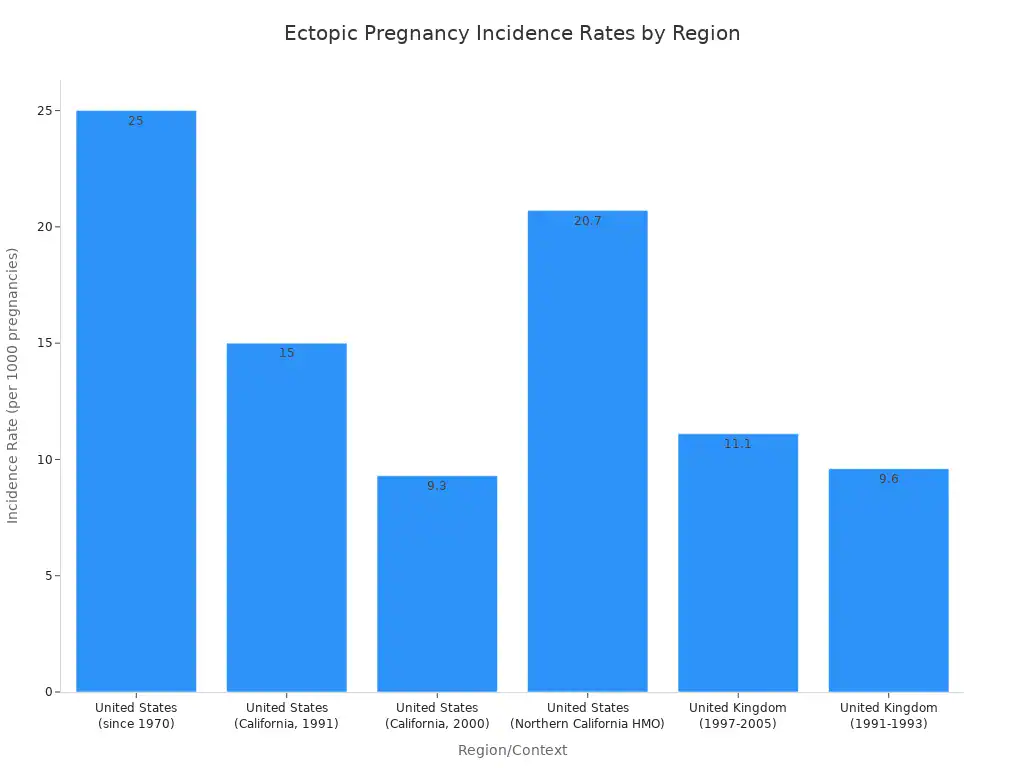
The incidence rate of ectopic pregnancy varies by region. In the United States, it has been around 25 per 1000 pregnancies since 1970, making up 1-2% of all pregnancies.
Region/Context | Incidence Rate (per 1000 pregnancies) | Percentage of all pregnancies | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|
United States (since 1970) | 25 | 1-2% | Since 1970 |
United States (California, hospital discharges) | 15 (1991), 9.3 (2000) | N/A | 1991-2000 |
United States (Northern California HMO) | 20.7 | ~2% | 1997-2000 |
United Kingdom | 11.1 | N/A | 1997-2005 |
United Kingdom | 9.6 | N/A | 1991-1993 |
Africa (hospital-based estimates) | 11-46 | 1.1-4.6% | N/A |
You might experience severe pain in your pelvis or abdomen, often sharp and stabbing on one side. This pain can range from mild to severe. It becomes more intense as the pregnancy progresses. You may also notice vaginal bleeding or spotting. This bleeding can be lighter or darker than a normal period. It can sometimes be mistaken for a regular period. Shoulder tip pain is a significant symptom. It often indicates internal bleeding and irritation of your diaphragm. This signals a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Dizziness or fainting can occur due to blood loss. These are critical symptoms requiring immediate medical attention. You might also feel pressure in your rectum. Abnormal bleeding or pain with a positive pregnancy test are early signs of an impending rupture. You need immediate medical attention for these symptoms.
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion happens when your testicle twists around the spermatic cord. This cuts off its blood supply. This condition is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to save the testicle.
Testicular torsion most commonly affects males aged 10 to 19 years. It also occurs in infants aged 0 to 1 year. You will experience sudden, intense, unilateral scrotal pain. This pain can sometimes radiate into your abdomen. Nausea and vomiting often accompany the pain. Your affected testicle may sit higher in the scrotum. It might also have an abnormal, horizontal position. The cremasteric reflex, which causes the testicle to rise when the inner thigh is stroked, is usually absent.
Doctors prioritize your airway, breathing, and circulation. They will give you IV fluids and medications for pain and nausea. You will be kept from eating or drinking in preparation for surgery. Doctors may attempt manual detorsion if surgery is delayed. This involves gently rotating the testicle away from the midline. Successful detorsion brings dramatic pain relief. Definitive treatment is surgical. Surgeons untwist the testicle as soon as possible to restore blood flow. The best outcomes happen if detorsion occurs within six hours.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in your kidneys. They can cause excruciating pain when they move into your urinary tract. This movement can block the ureters, which are the tubes connecting your kidneys to your bladder.
You might first notice a mild, persistent ache in your flank or back. This is a dull pain or pressure below your ribs. As the stone moves, the pain shifts downwards. You feel it in your lower abdomen, side, groin area, or even your inner thigh. This pain can be severe. It prevents you from finding a comfortable position. It can be stabbing or throbbing. The pain comes in waves and can last from 20 minutes to over an hour. Nausea and vomiting often accompany this severe pain. You might also experience changes in your urinary habits. These include increased urgency, increased frequency, and a painful or burning sensation during urination. You may see blood in your urine, making it pink, red, or brownish. Cloudy or foul-smelling urine suggests a possible infection. This is a common complication due to obstructed urine flow.
Severe Hernias
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through a weak spot in your muscle or tissue. Inguinal hernias can occur on your left side. They can cause constant pain in your lower left abdomen.
A hernia becomes urgent if it incarcerates or strangulates. An incarcerated hernia means the intestine or other organs get stuck. This causes pain and tenderness at the site. You might also experience nausea or vomiting. A strangulated hernia is more serious. The stuck contents lose their blood supply. This leads to extreme pain. You will also see signs of bowel obstruction. These include severe pain, vomiting, and an inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement. You might also have a fever or other symptoms of infection. A strangulated hernia is a surgical emergency. You need immediate treatment to prevent tissue death.
Ovarian Torsion And Cysts
Ovarian torsion happens when an ovary twists around its ligaments. This cuts off its blood supply. This condition is a gynecologic surgical emergency. It accounts for 2.7% of acute gynecologic complaints in some reports. It occurs in 2% to 15% of patients undergoing surgery for adnexal masses. It affects 10% to 22% of pregnant women.
You will experience sudden, severe pain in your pelvis. This pain is often sharp and localized to one side. Nausea and vomiting frequently accompany this pain. You might also notice abdominal swelling or bloating. This can result from an enlarged, twisted ovary. Fever is a less common symptom. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is rare but serious.
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs on your ovary. Small cysts often cause no symptoms. When they do, you might feel dull or sharp pelvic pain, bloating, or a sensation of fullness. If a cyst ruptures or causes torsion, you will experience sudden, severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. These are gynecological emergencies.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) includes conditions like Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s disease. These conditions cause chronic inflammation in your digestive tract.
Ulcerative colitis typically causes pain in your rectum or the lower left abdomen. This pain can range from mild to sharp, intense, and long-lasting. You might experience cramping or pain in your rectum or lower left abdomen during a bowel movement. Other symptoms include diarrhea or constipation, blood or mucus in your stool, and fatigue. Crohn’s disease usually causes pain in the lower right part of your abdomen. This is because it often affects the small intestine. However, Ulcerative Colitis specifically targets the colon, often starting in the rectum and spreading upwards. This makes pain in the lower left abdomen a key symptom for Ulcerative Colitis. These conditions require ongoing medical treatment. They can lead to severe complications if left unmanaged.
Less Urgent Causes Of Lower Left Abdominal Pain
You might experience pain in your lower left abdomen from less serious conditions. These causes are common. They usually do not need emergency medical care. Understanding these helps you tell them apart from urgent issues.
Gas And Indigestion
Gas and indigestion are common causes of discomfort. Gas is a normal part of digestion. Too much gas in your digestive tract causes pain, bloating, and discomfort. Indigestion often happens after you eat. Your stomach makes acid. This acid can irritate your esophagus, stomach, or bowel. While you usually feel indigestion in your upper abdomen, it can also affect your lower abdomen.
Several common causes lead to gas and indigestion. You might eat certain foods. Swallowing air by eating too quickly also causes gas. Indigestion or an upset stomach can contribute. Some people cannot digest certain foods. For example, celiac disease or lactose intolerance can cause problems. Regularly chewing gum or excessive smoking also causes gas. Overeating or eating too quickly leads to indigestion. Spicy and fatty foods can also cause it. Certain medications can also trigger indigestion. Lactose intolerance can cause pain in your lower left abdomen. Your body does not make enough lactase. This enzyme breaks down lactose in dairy products.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, is a common condition. It affects your large intestine. IBS causes abdominal pain and changes in your bowel habits. Doctors use specific criteria to diagnose IBS. You must have recurrent abdominal pain. This pain occurs at least one day per week for the last three months. This pain connects to two or more things. It relates to defecation. It also links to a change in how often you have a stool. Finally, it connects to a change in the stool’s appearance. These symptoms must be present for three months. They must also have started at least six months before diagnosis.
Menstrual Cramps And Ovulation
Many women experience menstrual cramps. These cramps cause pain in the lower abdomen. The pain can range from mild to moderate. Some women have severe pain. This pain can stop you from doing daily activities. Menstrual cramps usually start one to two days before your period. They are strongest about 24 hours after your period begins. The pain typically goes away within two to three days.
Ovulation pain is also called mittelschmerz. This pain happens when your ovary releases an egg. You often feel this pain in your lower abdomen or pelvis. It can be in the middle or on one side. If you feel it in your lower left abdomen, it might be a sharp or dull pain. This pain can last from a few minutes to a couple of days.
Constipation
Constipation is another common cause of lower left abdominal pain. You have constipation if you have fewer than three bowel movements per week. Your stools might be hard, dry, or lumpy. You may also have difficulty or pain when passing stools. Sometimes, you feel like you have not passed all your stool. Abdominal bloating or discomfort often comes with constipation. Many things cause constipation. These include not eating enough fiber or not drinking enough water. Lack of physical activity can also cause it. Changes in your daily routine or certain medications can also lead to constipation.
The Diagnostic Process For Abdominal Pain
You need to understand how medical professionals find the cause of your lower left abdominal pain. Doctors follow a clear process. This helps them identify the problem and plan your treatment.
Medical Evaluation
Your doctor starts by asking you many questions. They want to know about your pain. They ask when your pain started. This is the onset. They ask where your pain is located. You might point to your lower left abdomen. They ask how long you have had the pain. This is the duration. They also ask you to describe the pain. Is it sharp, dull, or cramping? These questions help them understand the character of your pain.
Your doctor also asks what makes the pain better or worse. They want to know if the pain spreads to other areas. They check if the pain follows any patterns. You will also answer questions about other symptoms. These include nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. For women, they ask about pelvic pain or abnormal discharge. They also ask about urination problems.
After asking questions, your doctor performs a physical exam. They check your general appearance and vital signs. They might press on your abdomen to find tender spots. They may perform a rectal exam. For women, a pelvic exam helps identify gynecologic issues.
Diagnostic Tests And Imaging
After the initial evaluation, your doctor may order tests. These tests help confirm a diagnosis.
Common diagnostic tests include:
Blood tests: These check for infection, anemia, or kidney problems.
Urine tests: These look for infections or kidney issues.
Stool tests: These can find blood or other problems in your stool.
Imaging tests: These create pictures inside your body.
For abdominal pain, a CT scan is often the first imaging test. It uses X-rays to create detailed images of your intestines and organs. CT scans are very good at finding problems like diverticulitis.
Ultrasound is another option. It uses sound waves. Doctors often use it for women of childbearing age. It helps check for conditions like ectopic pregnancy or ovarian torsion. MRI can also show problems like diverticulitis. It is useful for patients who cannot have CT scans.
Understanding Your Doctor’s Approach
Your doctor uses a systematic approach. They first check if you are critically ill. Then, they consider possible life-threatening diagnoses. They refine this list as they gather more information. They use your history and physical exam findings. This helps them narrow down the possibilities.
Doctors order tests based on how likely a condition is. They want to rule out serious diseases. They also want to confirm more likely diagnoses. They consider the cost and time involved. They also think about any potential harm from the tests. Your doctor documents their findings. They explain their reasoning for the diagnosis. They also create a treatment plan. This plan might involve medication or other treatment. If you are discharged, you receive clear instructions. These tell you when to seek medical attention again.
Lower left abdominal pain can range from benign to life-threatening. Prompt medical evaluation for urgent symptoms is crucial. This guide covered the urgent causes explained. Remember red-flag symptoms: severe pain, sudden onset, fever, or blood in stool. Never self-diagnose. You need professional medical attention. Trust your instincts. Seek help if you have concerns about your pain. Early intervention improves outcomes for any severe pain. Understanding these urgent causes explained helps you act quickly.
FAQ
What is the most common cause of urgent lower left abdominal pain?
Diverticulitis is a very common cause. It happens when small pouches in your colon get inflamed or infected. You will feel constant pain in your lower left side. This condition often needs medical treatment.
When should I seek immediate medical help for lower left abdominal pain?
You should seek immediate help if you have severe, sudden pain. Also look for fever, persistent vomiting, or blood in your stool. These are red flag symptoms. They mean you need urgent medical treatment.
Can ovarian cysts cause urgent pain in the lower left abdomen?
Yes, they can. If an ovarian cyst ruptures or causes ovarian torsion, you will feel sudden, severe pain. This is a medical emergency. It requires prompt medical treatment to prevent complications.
What is the diagnostic process for lower left abdominal pain?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam. They may order blood tests, urine tests, or imaging like a CT scan. These steps help them find the cause and decide on the best treatment for you.