
You might notice mangosteen popping up more often in stores and health circles lately due to its impressive health benefits. People call it the queen of fruits for its unique taste and vibrant look.
The global mangosteen market keeps growing, especially in North America, Asia Pacific, and places like Japan and India, where health trends push demand for this tropical superfruit.
In Canada, urban centers love adding mangosteen to their diets, while the U.S. sees a surge thanks to health-conscious shoppers seeking its health benefits.
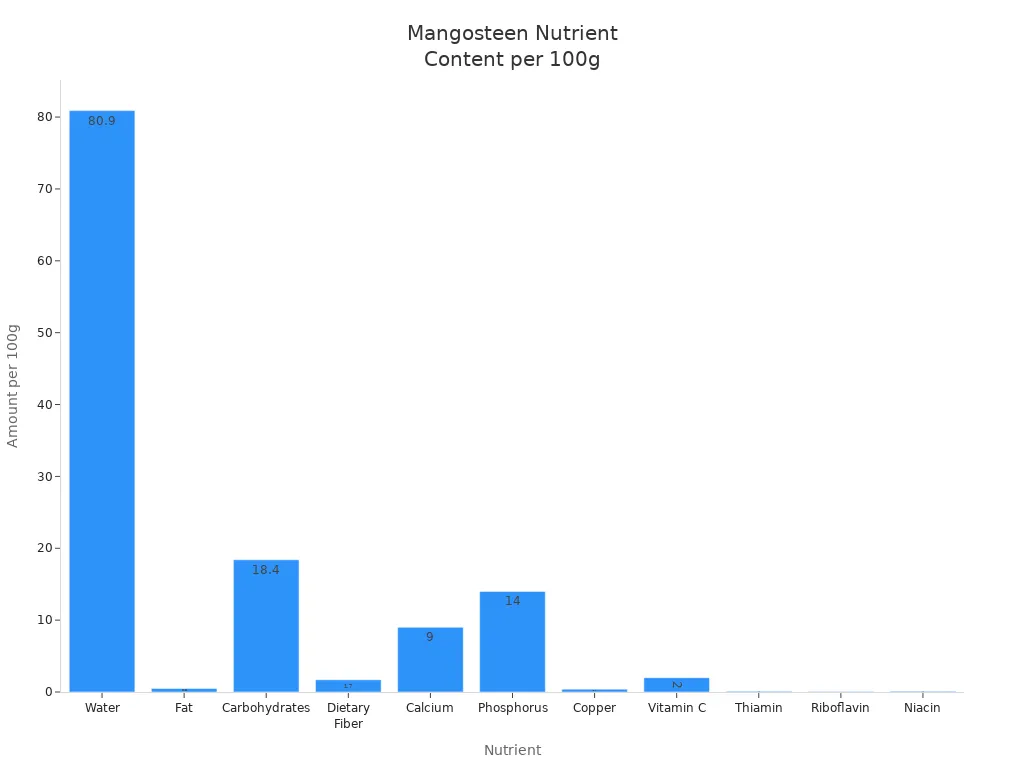
Take a look at what’s inside mangosteen:
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Water | 80.9 g |
Carbohydrates | 18.4 g |
Dietary Fiber | 1.7 g |
Vitamin C | 2 mg |
Xanthones | Various |
You get powerful antioxidants called xanthones in mangosteen, which contribute to its health benefits by helping your body fight free radicals and keep you feeling your best.
Key Takeaways
Mangosteen is rich in antioxidants, particularly xanthones, which help protect your cells from damage and may slow aging.
This tropical fruit supports immune health, thanks to its vitamin C and xanthones, making it easier for your body to fight off illness.
Regular consumption of mangosteen can promote heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of heart disease.
Mangosteen aids digestion and can help relieve common digestive issues, making it a great addition to your diet.
Incorporate mangosteen into your meals by adding it to smoothies, salads, or enjoying it fresh for a delicious health boost.
What Is Mangosteen?
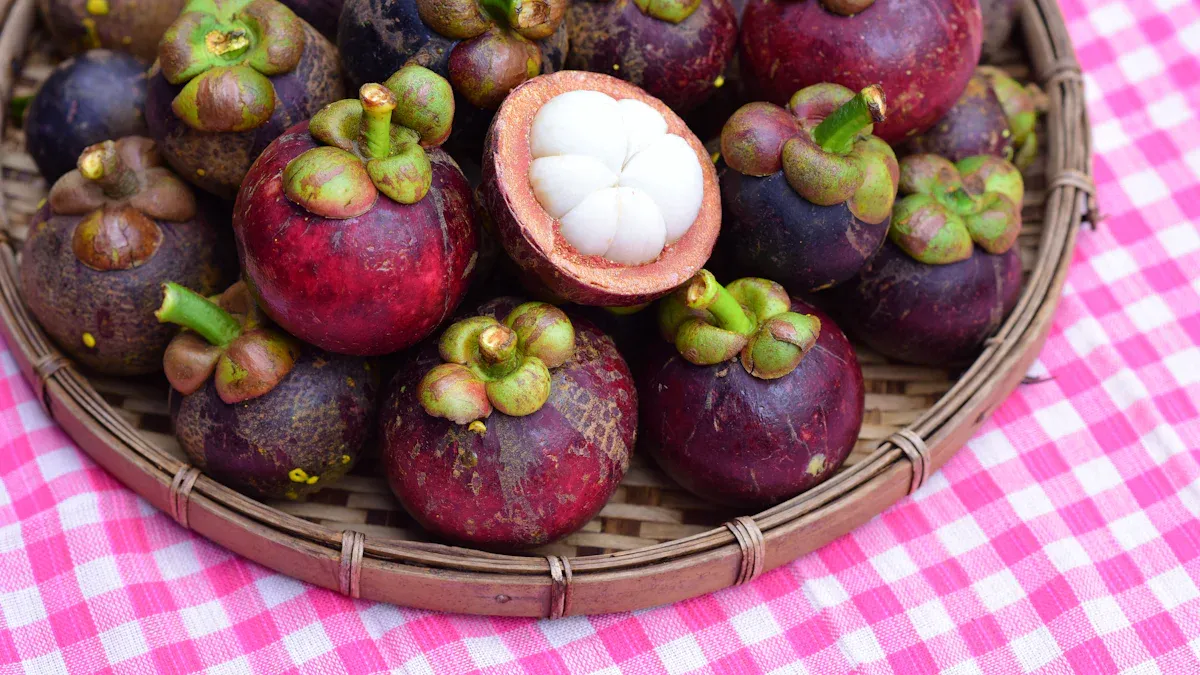

Origin
You might wonder where mangosteen comes from. This tropical fruit has a fascinating background.
Mangosteen’s botanical name is Garcinia mangostana L.
It belongs to the Clusiaceae family.
People often call it the purple mangosteen.
The fruit is native to Southeast Asia, especially the islands stretching from the Malay Peninsula to Borneo.
Farmers grow mangosteen in places like Java, Sumatra, Indochina, and the southern Philippines.
If you travel through Malaysia, Indonesia, or Thailand, you’ll spot mangosteen trees in lush, humid areas. These trees thrive in tropical climates and don’t do well in cold weather. You can see why mangosteen feels so special—it only grows in certain regions.
Did you know? Mangosteen trees stay green all year and can live for decades. Some people even call them “evergreen treasures” of the tropics.
Unique Qualities
Mangosteen stands out from other fruits in many ways.
The fruit looks like a small, round ball with dark purple skin and bright white flesh inside.
When you taste mangosteen, you get a sweet flavor with a hint of sourness. Many people say it’s one of the best-tasting fruits in the world.
Mangosteen contains special bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, xanthones, and bioflavonoids. These natural chemicals give mangosteen its unique properties.
Scientists have found that mangosteen’s compounds show anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and even anti-tumor effects.
You don’t just enjoy mangosteen for its taste. You also get a boost from its natural ingredients. The fruit’s antioxidants, especially xanthones, help protect your body and support your immune system. That’s why mangosteen earns its reputation as the queen of fruits.
Why Queen of Fruits?
History
You might wonder why people call mangosteen the queen of fruits. The story behind this royal nickname is pretty interesting. Over the years, many legends and stories have popped up about how mangosteen got its title. Some say Queen Victoria loved this fruit, but there is no real proof for that. Instead, the name likely comes from local traditions and famous explorers who spread the word about mangosteen’s special qualities.
Here’s a quick look at what history says:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Historical Reference | David Fairchild popularized the title ‘Queen of Tropical Fruit’ in the early 20th century, not directly linked to Queen Victoria. |
Folklore | The title may stem from local expressions in Thailand or Malaysia, possibly dating back to colonial times. |
Misattribution | Many claims about Queen Victoria’s connection to the mangosteen lack historical proof and are based on conjecture. |
You can see that the queen of fruits nickname has more to do with tradition and admiration than with any real royal connection. In Southeast Asia, people have always treated mangosteen as a luxury. They often served it to important guests as a sign of respect and good hospitality.
Distinct Features
What makes mangosteen stand out from other fruits? First, you notice its look. The thick purple skin and bright white flesh make it one of the most eye-catching fruits you’ll ever see. No other fruit has this exact color combination. When you open a mangosteen, you get a sweet smell that hints at the treat inside.
The taste is something special, too. People often describe it as a mix of pineapple, peach, and lemon. You get a perfect balance of sweetness and gentle acidity. Every bite feels refreshing and satisfying. That’s why so many people fall in love with mangosteen after just one try.
Mangosteen is not just about looks and taste. It also contains powerful antioxidants called xanthones, plus vitamin C and fiber. These nutrients help your body stay healthy and make mangosteen a true tropical superfruit. Because mangosteen was rare and hard to find, only royal families could enjoy it in the past. Today, you can try this fruit and feel like royalty, too.
Tip: If you want to impress your friends or family, serve mangosteen at your next gathering. It’s a symbol of luxury and good taste in many cultures. 🍈
Health Benefits of Mangosteen
Mangosteen packs a punch when it comes to health benefits. You get more than just a tasty treat—this fruit delivers a wide range of nutrients and phytonutrients that help you feel your best. Let’s explore the top health benefits of mangosteen and see why so many people call it a superfruit for promoting overall wellness.
Rich in Antioxidants
You might hear people say mangosteen is rich in antioxidants. That’s true! The fruit contains powerful antioxidants called xanthones, which help protect your cells from damage. These compounds, like α-mangostin and γ-mangostin, fight off harmful free radicals and support your well-being.
Here’s a quick look at how mangosteen’s antioxidants compare:
Compound | Antioxidant Activity | Comparison |
|---|---|---|
α-Mangostin | Scavenges singlet oxygen, O2•-, ONOO- | Major xanthone in mangosteen peel |
P1 | Highest DPPH• and HO• scavenging activity | Higher than Trolox and BHA |
P2 | Higher O2•- scavenging activity than P1 | Higher than Trolox |
P3 | Higher O2•- scavenging activity than P1 | Higher than Trolox |
You get the most abundant antioxidants from xanthones, including α-mangostin, γ-mangostin, β-mangostin, gartanin, and garcinones. These potent antioxidant properties help keep your body healthy and may slow down aging.
Immune Support
Mangosteen supports immune function in several ways. You get immune-boosting properties from its vitamin C and xanthones. Studies show that people who consume mangosteen experience increased T-helper cell frequency and improved self-appraisal of health status.
Measurement | Experimental Group | P-value |
|---|---|---|
Peripheral T-helper cell frequency | Increased | 0.020 |
Serum C-reactive protein concentration | Reduced | 0.014 |
Serum complement C3 concentration | Increased | 0.017 |
Serum IL-1alpha concentration | Increased | 0.006 |
Self-appraisal of health status | Improved | 0.001 |
You can see that mangosteen helps your immune system stay strong, making it easier for you to fight off illness and stay healthy.
Heart Health
You want a healthy heart, right? Mangosteen offers benefits for your cardiovascular system. The fruit’s antioxidants and anti-inflammatory effects help reduce inflammation, which is linked to heart disease. Clinical trials show that drinking mangosteen juice can lower C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker for inflammation.
Study Focus | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Daily consumption of a mangosteen-based drink | Improved antioxidant and anti-inflammatory biomarkers | Suggests potential benefits for cardiovascular health |
CRP reduction in subjects consuming XanGo Juice | Statistically significant reduction in CRP | Indicates a potential decrease in heart disease risk |
When you add mangosteen to your diet, you may help lower your risk of heart problems and keep your heart healthy.
Digestive Aid
Mangosteen supports digestive health and helps with common issues like diarrhea and abdominal pain. People in Southeast Asia have used mangosteen rind for centuries to soothe the digestive tract. The fruit’s anti-inflammatory properties and fiber content make it a great choice for improving digestion.
If you want to feel comfortable after meals, mangosteen can help your digestion and keep your stomach happy.
Anti-Inflammatory
You get strong anti-inflammatory effects from mangosteen. The fruit contains α-mangostin, flavonoids, and terpenoids, which work together to reduce inflammation in your body.
Compound | Type | Efficacy Evidence |
|---|---|---|
α-mangostin | Xanthone | Shown to reduce inflammation and promote wound healing |
Flavonoids | Flavonoid | Help lower inflammatory responses |
Terpenoids | Terpenoid | Support anti-inflammatory effects |
These anti-inflammatory properties help you recover faster from injuries and may lower your risk of chronic diseases.
Skin Health
Mangosteen enhances skin health and helps you maintain healthy skin. The fruit’s antioxidants and anti-inflammatory effects protect your skin from damage and reduce inflammation. Studies show that mangosteen peel has higher antioxidant levels than many other fruit peels, and mangosteen extract can curb acne-causing inflammation.
Study Source | Findings |
|---|---|
Journal of Food Science and Technology | Mangosteen peel has higher levels of antioxidants than other fruit peels |
Fitoterapia | Mangosteen extract curbed acne-causing inflammation and neutralized free radicals |
PMC Article | Mangosteen peel extract may serve as an anti-aging agent |
You can enjoy the benefits of mangosteen for glowing, youthful skin.
Weight Management
If you’re looking for weight loss support, mangosteen may help. Studies show that mangosteen extract improves insulin sensitivity and reduces fat accumulation. In one study, obese female patients experienced weight reduction and improved insulin response after taking mangosteen extract for 26 weeks.
Mangosteen extract improved insulin sensitivity in obese patients.
Alpha-mangostin inhibits enzymes that help store fat.
Participants in the mangosteen group saw a trend toward greater weight loss.
Inflammatory markers were reduced, which is important for managing obesity.
You can use mangosteen as part of a healthy lifestyle to support weight management and well-being.
Blood Sugar Support
Mangosteen helps regulate blood sugar levels and may lower your risk of diabetes. Several studies found that mangosteen extracts decrease fasting blood glucose and improve insulin secretion in diabetic mice and humans.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Bi et al., 2023 | Mangosteen extracts showed hypoglycemic activity in rodent models |
Watanabe et al., 2018 | Improved insulin resistance and inflammatory status in obese patients |
Husen et al., 2019 | Decreased fasting blood glucose and improved insulin secretion |
Karim et al., 2017 | Significant decrease in plasma glucose and lipid profiles in diabetic mice |
Muniroh et al., 2021 | Reduced inflammatory markers and improved antioxidant levels in diabetic rats |
You can use mangosteen to help keep your blood sugar levels in check and support your overall health.
Brain Health
Mangosteen offers benefits for your brain health. Research shows that mangosteen pericarp reduces cognitive dysfunction and enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in mice. Dietary supplementation with mangosteen pericarp in Alzheimer’s models showed neuroprotective and antioxidative effects.
Mangosteen pericarp reduced cognitive dysfunction in mice.
Supplementation helped mitigate cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s models.
Water-soluble mangosteen extract improved cognitive function in patients with mild to moderate impairment.
You can support your memory and mental clarity by adding mangosteen to your diet.
Potential Anti-Cancer
Mangosteen may offer potential anti-cancer effects. Laboratory studies show that mangosteen pericarp extract is cytotoxic to several cancer cell lines, including breast, liver, cervical, and skin cancer cells. The extract induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, which may help prevent cancer growth.
Study Focus | Cell Line/Model | Findings |
|---|---|---|
Mangosteen pericarp extract | MCF-7 breast cancer cells | Induced apoptosis, cytotoxic at 45 μg/mL |
Mangosteen pericarp extract | SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells | IC50 of 15 μg/mL (ethanolic), 9.25 μg/mL (methanolic) |
Mangosteen pericarp extract | HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cells | Cytotoxic under normoxia and hypoxia |
Mangosteen pericarp extract | HeLa and H357 cells | Decreased proliferation, induced apoptosis |
Mangosteen pericarp extract | A-431 and SK-MEL-28 skin cancer cells | Induced apoptosis, cell cycle arrest at G1 phase |
You get the benefit of powerful antioxidants and anticancer effects when you eat mangosteen, making it a smart choice for promoting overall wellness.
Tip: If you want to enjoy the health benefits of mangosteen, try adding it to smoothies, salads, or eat it fresh. You’ll get a delicious boost for your well-being.
How to Eat Mangosteen

Choosing Mangosteen
You want the best mangosteen for taste and nutrition. When you pick mangosteen at the store or market, look for these signs:
Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
Skin Color | Deep purple with an even tone means ripe mangosteen. |
Texture | The rind should feel slightly soft but firm. Avoid fruit that feels rock-hard or mushy. |
Bottom Flower Examination | Count the petals on the bottom. More petals often mean more edible segments inside. |
Common Mistakes | Skip mangosteen with damaged skin or uneven color. Overripe or underripe fruit won’t taste as good. |
Quality Maintenance | Sellers keep mangosteen fresh by sorting, grading, and packaging carefully. |
Tip: Gently press the skin. If it gives a little but stays firm, you’ve found a good one! 🍈
Eating Fresh
You can enjoy mangosteen in many tasty ways. The classic method is to eat it fresh. Just slice around the thick purple rind, twist it open, and scoop out the juicy white segments. The flavor is sweet and slightly tart, making it a favorite snack.
Here are some popular ways to eat fresh mangosteen:
Add mangosteen to fruit salads with durian or other tropical fruits.
Toss mangosteen segments into leafy green salads for extra sweetness.
Mix mangosteen with spicy Thai salads to mellow out the heat.
Blend mangosteen into smoothies for a tropical twist.
Pair mangosteen with iced or hot tea. You can even use the rind to make tea.
Try dehydrated or freeze-dried mangosteen as a crunchy snack or baking ingredient.
Use mangosteen in cocktails, sorbets, or creamy desserts like panna cotta.
Note: Mangosteen tastes best when you eat it fresh. The juicy segments burst with flavor and nutrients.
Juice and Supplements
You might see mangosteen juice and supplements at health stores. Mangosteen juice is packed with xanthones, which help fight inflammation and support your immune system. Drinking mangosteen juice may help regulate blood sugar and protect against chronic diseases. If you add a little healthy fat to your meal, your body absorbs these nutrients even better.
Supplements and extracts offer concentrated bioactive compounds like anthocyanins, polyphenolics, and tannic acids. These support your health in different ways, such as fighting germs and reducing swelling. Eating whole mangosteen gives you fiber and a mix of nutrients, while juice and supplements provide higher levels of certain compounds.
Mangosteen juice is rich in xanthones and may help with inflammation.
Supplements contain concentrated bioactive compounds.
Whole mangosteen offers fiber and a unique blend of nutrients.
The way your body absorbs these nutrients can change depending on how you eat mangosteen.
Tip: Try different forms of mangosteen to see what you like best. Each option brings its own benefits!
Intake Tips
Serving Size
You might wonder how much mangosteen you should eat each day. Nutrition experts suggest that most healthy adults enjoy between 1 to 3 mangosteens daily. This amount gives you plenty of antioxidants and vitamins without too much natural sugar or fiber. You get the health benefits without overdoing it.
Eating 1 to 3 mangosteens a day is safe for most adults.
This serving size supports your overall health.
You get enough nutrients without worrying about excess sugar.
If you are new to mangosteen, start with one fruit. See how your body feels. You can add more as you get used to the taste and texture. Remember, fresh mangosteen tastes best, but you can also try juice or supplements if fresh fruit is not available.
Tip: Listen to your body. If you feel great after eating mangosteen, you are on the right track!
Best Practices
You have many ways to add mangosteen to your meals. Try these easy ideas to make the most of this tropical fruit:
Use freeze-dried mangosteen in smoothies, oatmeal, or yogurt for a sweet boost.
Sprinkle fresh or dried mangosteen over salads to add a tropical twist.
Mix mangosteen into baked goods as a natural sweetener.
Blend mangosteen fruit powders into smoothies or yogurt for extra flavor.
Add mangosteen peel flour to salads or juices for more fiber.
Enjoy mangosteen concentrate mixed with water for a refreshing drink.
You can get creative in the kitchen. Mangosteen pairs well with both sweet and savory dishes. Try it in desserts, drinks, or even as a topping for breakfast foods.
Note: Try different forms of mangosteen to see what you like best. Each option brings its own unique taste and health benefits! 🍈
Precautions
Allergies
You might feel excited to try mangosteen, but you should check for allergies first. Some people react to tropical fruits, and mangosteen is no exception. If you notice itching, swelling, or trouble breathing after eating mangosteen, stop right away and talk to your doctor. Allergic reactions can happen even if you have never had problems with other fruits. Always start with a small amount if you are new to mangosteen.
Tip: If you have a history of fruit allergies, keep an eye out for any unusual symptoms after eating mangosteen. Safety comes first! 🍈
Who Should Avoid
Not everyone can enjoy mangosteen safely. Certain health conditions and medications make mangosteen risky for you. Here are some groups who should avoid mangosteen:
People taking Donepezil for Alzheimer’s disease. Mangosteen may interact with this medication.
Individuals with lactic acidosis. Mangosteen can make symptoms like fatigue and nausea worse.
Anyone with stomach acid problems. Eating too much mangosteen may cause bloating, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Surgical patients. Mangosteen has anticoagulant effects, which can increase bleeding risk before or after surgery.
Patients using blood-thinning drugs. Mangosteen may raise the chance of bruising and bleeding.
Cancer patients. Mangosteen could lower the effectiveness of chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Always check with your doctor first.
If you fall into one of these groups, talk to your healthcare provider before adding mangosteen to your diet.
Medication Interactions
Mangosteen can interact with several types of medication. You should know about these possible effects before you eat the fruit or take supplements. Here’s a quick look at some known interactions:
Medication Type | Interaction Description |
|---|---|
Chemotherapeutic drugs | Mangosteen may interact with drugs such as anthracyclines, platinum compounds, and alkylating agents. |
Antihistamines | There may be an additive effect when taken with mangosteen. |
Drug metabolism | Mangosteen may inhibit hepatic CYP-450 enzyme activities, potentially interfering with drug metabolism. |
If you take any of these medications, ask your doctor if mangosteen is safe for you. Mixing mangosteen with certain drugs can change how your body processes medicine or increase side effects.
Note: Always check with your healthcare provider before trying new foods or supplements, especially if you take prescription medication. Your health matters most!
Mangosteen stands out for its sweet taste, vibrant look, and unique bioactive compounds. You get a fruit packed with xanthones that may help your memory, heart, and mood. Take a look at some key findings:
Benefit | What Studies Show |
|---|---|
May protect brain cells in mice | |
Heart Health | Can boost HDL cholesterol |
Anti-inflammatory | May lower CRP levels |
Mood Improvement | Shows promise for easing depression |
If you want to try mangosteen, pick ripe fruit with a deep purple rind. Always check with your healthcare provider before using supplements, especially if you have health concerns or take medication. Enjoy mangosteen in salads, smoothies, or as a fresh snack, but remember to stay safe!
FAQ
Can you eat mangosteen seeds?
You should not eat mangosteen seeds. The seeds taste bitter and feel tough. Stick to the juicy white flesh for the best flavor and nutrition.
How do you store fresh mangosteen?
You can keep fresh mangosteen at room temperature for a few days. If you want it to last longer, put it in the fridge. The cool air helps keep the fruit fresh.
Is mangosteen safe for kids?
Kids can enjoy mangosteen in small amounts. The fruit is soft and sweet. Always remove the rind and seeds before serving. Watch for allergies if your child tries mangosteen for the first time.
Can you freeze mangosteen?
Yes, you can freeze mangosteen. Peel the fruit and place the segments in a sealed container. Frozen mangosteen works well in smoothies or desserts.
Does mangosteen taste like other fruits?
Mangosteen has a unique flavor. You might notice hints of peach, pineapple, and citrus. The taste is sweet with a little tartness. Many people call it the best-tasting tropical fruit.







