The superfoods market is booming, with Fortune Business Insights projecting a 7.70% Compound Annual Growth Rate from 2025 to 2032. Plant-based nutrition also garners increasing interest. Amidst this trend, an ancient superfood, sacha inchi, receives modern recognition. These sacha inchi nuts, often called “Inca peanuts” or “Inca nut seeds,” originate from the Amazon rainforest. Sacha inchi boasts an impressive nutritional profile, offering abundant Omega-3s and protein crucial for good health and overall nutrition.
Key Takeaways
Sacha inchi nuts are ancient seeds from the Amazon rainforest, also called “Inca peanuts.”
These nuts are rich in healthy Omega-3 fats and complete protein, which are good for your body.
Eating sacha inchi can help your heart, brain, and digestion, and it can also help manage your weight.
Sacha inchi is a superfood because it has many nutrients and is grown in a way that helps the environment.
You can eat sacha inchi as roasted seeds, use its oil, or add its powder to your food, but never eat them raw.
What Are Sacha Inchi Nuts

Origin and History
Sacha inchi, also known as Plukenetia volubilis, is a perennial plant. It is native to parts of South America and the Caribbean. Indigenous groups in Peru traditionally consumed it. They called it mountain peanut or Inca nut. This sacha inchi is native to the Peruvian jungle. Ancient pre-Inca cultures, like the Mochica and Chimú civilizations, cultivated it. Archaeological findings of pre-Inca utensils show its historical importance. The plant’s common name in the native Quechua language means ‘false peanut’. This reflects its early use as an edible nut by tribes such as the Chanka and Mochica-Chimú. Sacha inchi is mainly found in the Amazon region. Countries like Peru, Colombia, and Brazil grow it. Its history is deep-rooted in Amazonian indigenous communities. There, it has been a crucial crop for their diet and economy.
The Sacha Inchi Plant
The sacha inchi plant (Plukenetia Volubilis L.) belongs to the Euphorbiaceous family. It is a perennial, oleaginous plant. This semi-woody plant typically grows to about 2 meters tall. The plant produces both flowers and fruit capsules around 8 months after planting. Its fruit capsule is star-shaped, measuring about 3–5 cm. It changes color from green to blackish brown as it matures. Each fruit capsule contains 4–6 edible dark brown oval sacha inchi seeds. These seeds are 1.5 to 2 cm in size. The dried fruit capsule has a non-edible shell (30–35%) and edible kernels (65–70%). These kernels are the sacha inchi seeds. The plant thrives in warm climates, between 10–36 °C. It needs significant annual rainfall, 850–1000 mm. It prefers well-drained acidic soil, like sandy or clay loams. It grows at altitudes from 200–1500 meters.
Appearance and Taste
Sacha inchi nuts are actually toasted seeds. They have a crisp, nutty flavor. This flavor is not overpowering when mixed with other foods. Sacha inchi nuts offer a rich nuttiness with a savory profile. Many compare it to a blend of macadamia and soybean. They also have a unique umami essence. This comes from their healthy Omega fatty acid content. These nuts, sometimes called sacha peanuts or mountain peanuts, are about the size of a large peanut. They grow inside geometric pods. These pods look appealing before cracking them open. When you first crunch them, the taste is mostly nutty. Some people notice a distinct fishy flavor after about 10 seconds. Others describe a buttery finish. The seeds are rich in protein, fiber, and heart-healthy unsaturated fats. They also contain important micronutrients like phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and zinc.
Nutritional Profile of Sacha Inchi

Sacha inchi offers an impressive nutrient profile. This ancient superfood provides many essential components for good health. A 100-gram serving of sacha inchi nuts contains:
Calories: 700
Fat: 50 g
Omega 3: 47% – 51%
Omega 6: 34% – 37%
Omega 9: 9% – 11%
Salt: 0 g
Carbohydrates: 10 g
Fiber: 10 g
Sugar: 0 g
Protein: 30 g
Calcium: 200 mg
Iron: 3.6 mg
This rich nutrient profile makes sacha inchi a valuable addition to many diets.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Sacha inchi stands out for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids. These are essential heart healthy fats. The oil from sacha inchi contains 50.5% omega-3. This makes it one of the richest plant-based sources.
Source | Omega-3 Content |
|---|---|
Sacha Inchi Oil | 50.5% |
Sacha Inchi Residue | Highest |
Candlenut | Second Highest |
Black Beans | Third Highest |
Sacha inchi also provides a balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids. The ideal omega-6 to omega-3 ratio for health is around 1:1. Sacha inchi naturally contains this ideal balance. It has approximately 3.5g of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and 4g of Omega-6 Fatty Acids. This gives a ratio of about 1:1.14. This balanced ratio is important for overall health.
Plant-Based Protein
Sacha inchi is an excellent source of plant-based protein. It contains approximately 30 grams of protein per 100 grams. This makes it a significant protein source. The protein in sacha inchi is complete. This means it contains all nine essential amino acids the body needs.
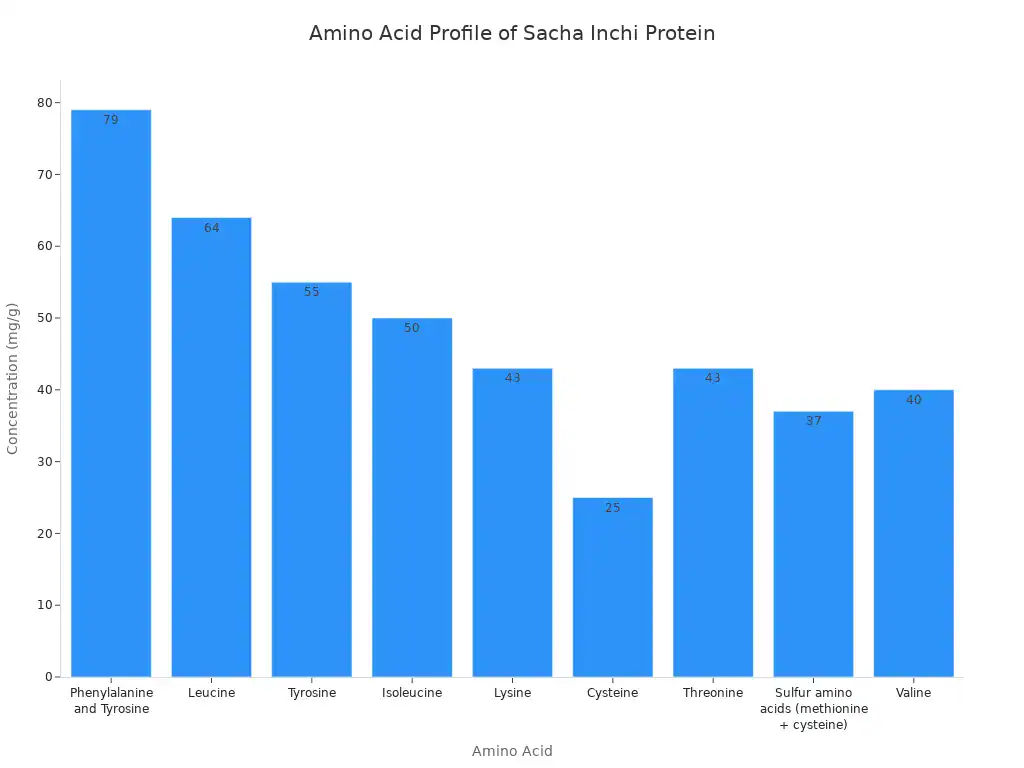
Sacha inchi protein has a diverse amino acid profile:
Amino Acid | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
Glutamic acid | 7.71 |
Aspartic acid | 6.83 |
Glycine | 6.31 |
Arginine | 6.13 |
Leucine | 4.03 |
Valine | 3.46 |
Serine | 3.48 |
Total lysine | 2.95 |
Tyrosine | 2.87 |
Isoleucine | 2.73 |
Threonine | 2.65 |
Proline | 2.29 |
Alanine | 2.04 |
Phenylalanine | 1.42 |
Histidine | 1.17 |
Methionine | 0.68 |
Sacha inchi is particularly rich in aspartate and glutamine amino acids. It also has higher levels of tryptophan, arginine, and glycine compared to soy flour. The seeds contain a water-soluble storage protein (albumin). This protein provides all essential amino acids in amounts suitable for human needs.
Vitamins and Minerals
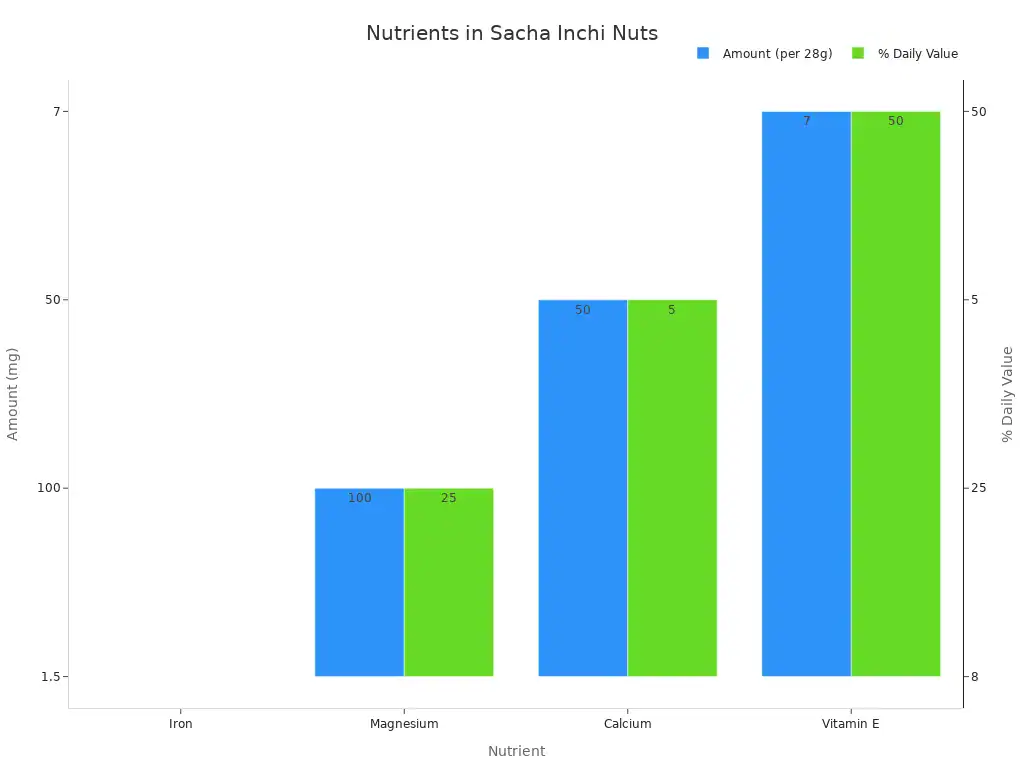
Sacha inchi nuts provide several important vitamins and minerals. These micronutrients contribute to overall health. A 28-gram serving offers:
Nutrient | Amount (per 28g) | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
Iron | 1.5mg | 8% |
Magnesium | 100mg | 25% |
Calcium | 50mg | 5% |
Vitamin E | 7mg | 50% |
Sacha inchi is also a source of potassium and zinc. These minerals play vital roles in many bodily functions.
Antioxidant Content
Sacha inchi seeds contain powerful antioxidants. These compounds help protect the body from damage. The seeds provide:
Tocopherols: specifically gamma (γ) and delta (δ)-tocopherols.
Phenolic compounds
Condensed tannins
Hydrolysable tannins
Lignans
Flavonoids
The shell of sacha inchi also contains phenolic compounds and other antioxidants. These antioxidants contribute to the overall health benefits of sacha inchi.
Sacha Inchi Benefits
This ancient superfood offers numerous benefits for overall well-being.
Heart Health Support
This plant provides significant health benefits for the heart. Its essential unsaturated fatty acids improve metabolic syndrome diseases. These include obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver. Studies show supplements from this plant lead to lower triglyceride accumulation. They also reduce fat droplet distribution in the liver. This suggests it does not induce fatty liver. The oil regulates cholesterol levels. It lowers total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol. It also reduces blood pressure. It significantly increases HDL (good) cholesterol. This reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease. This plant contains essential fatty acids. These include omega-3 (α-linolenic acid), omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids. It also has tocopherols, flavonoids, phytosterols, lignans, and phenyl alcohols. These compounds are associated with cardiovascular health benefits. Oil supplementation improves serum lipid profiles in humans. It increases HDL and decreases LDL. The high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidant compounds in the oil offers vascular benefits. It reduces oxidative stress. Significant improvements were observed in total cholesterol, LDL-C, and HDL-C in the oil group. This happened after 12 weeks. Four months of consuming the oil significantly reduced total cholesterol, LDL-C, non-HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, VLDL, and NEFAs. This was seen in hypercholesterolemic patients. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is abundant in the oil. It modulates lipid metabolism. It improves lipid homeostasis. It increases fatty acid β-oxidation. It does this by upregulating peroxisome-activated receptor-ɑ. It also downregulates sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the oil contribute to balanced lipid profiles. Oil consumption can mitigate the increase in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) entry into circulation. It suppresses the correlation between LPS and triglycerides. Omega-3 PUFAs also influence lipolysis. They modulate perilipin and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL). This increases fatty acid hydrolysis. Lipoprotein lipase enzyme activity is enhanced by the oil. This reduces chylomicron and VLDL-triacylglycerol levels in the blood. This leads to a lipid-lowering effect. LDL-cholesterol was reduced. HDL-cholesterol was increased with oil consumption. Serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels were lowered. A study found a significant reduction in total cholesterol and LDL-C. It also found a considerable increase in HDL-C. This happened after 4 months of oil administration. Consumption of sacha inchi seed oil improved liver function. It reduced cholesterol and triglycerides. It increased HDL levels. These are truly heart healthy fats.
Brain Function Boost
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in sacha inchi offer neuroprotective properties. The oil shows significant anticonvulsant effects. This is likely due to its ability to reduce free radicals. It also enhances GABA levels in the brain. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are crucial for brain development. They support cognitive health. They also offer therapeutic benefits in managing neurological disorders. These fatty acids help with chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. The omega-3s in this plant directly reduce inflammation in the brain. This reduction in inflammation improves mood. It enhances attention. It leads to a “sharper mind.” This mind is better equipped for complex information processing. An Italian study showed participants experienced these benefits after one month of omega-3 supplementation. The oil demonstrates neuroprotective effects. This includes anticonvulsant activity. It reduces free radicals and improves GABA levels in the brain. This mechanism was observed in an experimental model. A maximum dose of the oil significantly reduced seizure levels, frequency, and duration.
Weight Management Aid
Sacha inchi protein supports weight management. It has a high protein content. It also has a favorable amino acid profile. It induces satiety. Protein-rich diets promote fullness. They reduce overall calorie intake. They help maintain lean muscle mass during caloric deficit. The protein is rich in dietary fiber. This fiber aids in appetite control. The seeds are rich in complete proteins and fiber. Each serving provides a substantial amount of fiber. This fiber aids in promoting digestive health. It maintains stable blood sugar levels. Its high protein and fiber content promote satiety. It reduces cravings. This makes it a good snack option for weight management. Four grams of fiber per serving supports gut health. It ensures regular digestion. It promotes fullness.
Digestive Health Promotion
Sacha inchi protein (SIP) promotes intestinal health. It alters the composition of intestinal flora. It regulates metabolic activities. SIP is rich in amino acids, including arginine. It decreases harmful intestinal bacteria. It increases beneficial ones. Sacha inchi oil also alleviates intestinal flora dysbiosis. Both the protein and oil components of this plant contribute to digestive health benefits.
Skin and Hair Enhancement
This plant offers benefits for skin and hair. High levels of vitamin E and antioxidants make it excellent for anti-aging skincare products. Vitamin E nourishes and protects the skin. Antioxidants protect against environmental damage. They promote cell regeneration. For hair, high levels of protein strengthen and repair damaged hair. Healthy fats moisturize and nourish the scalp. People can use the seeds in various ways. They can mix them with water to create a face mask. They can combine them with coconut oil or avocado oil for a hair mask. It can also be part of a body scrub. It can be blended into a lip balm. These applications highlight its versatile benefits.
Inflammation Reduction
This plant combats inflammation. It increases circulating levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the blood. The oil contains Omega 3 (ω-3) fatty acids. These constitute up to 53% of its total fatty acids. Specifically, it contains α-linolenic omega 3 (ALA ω-3) fatty acids. These range from 45% to 54%. These ω-3 fatty acids significantly reduce the production of proinflammatory molecules. They inhibit or lessen inflammatory responses. This is one of its key health benefits.
Why Sacha Inchi is a Superfood
Many foods are called “superfoods” today. The food industry often uses this term for marketing. People also use it on social media. This makes many foods popular.
In fact, there is not a clear and legal definition of ‘superfoods’; nowadays, many foodstuffs are included in this group by the marketing of the food industry. The term is commonly used in informal communication, on social media and by popular influencers, which increases the popularity of a wide variety of foods.
However, superfoods usually share common traits:
They are rich in macro- and micronutrients.
They help human health and prevent illness.
Their properties are natural.
They are often linked to indigenous people and old farming ways.
Sacha inchi meets these criteria. It offers a powerful nutritional profile.
Nutrient Density
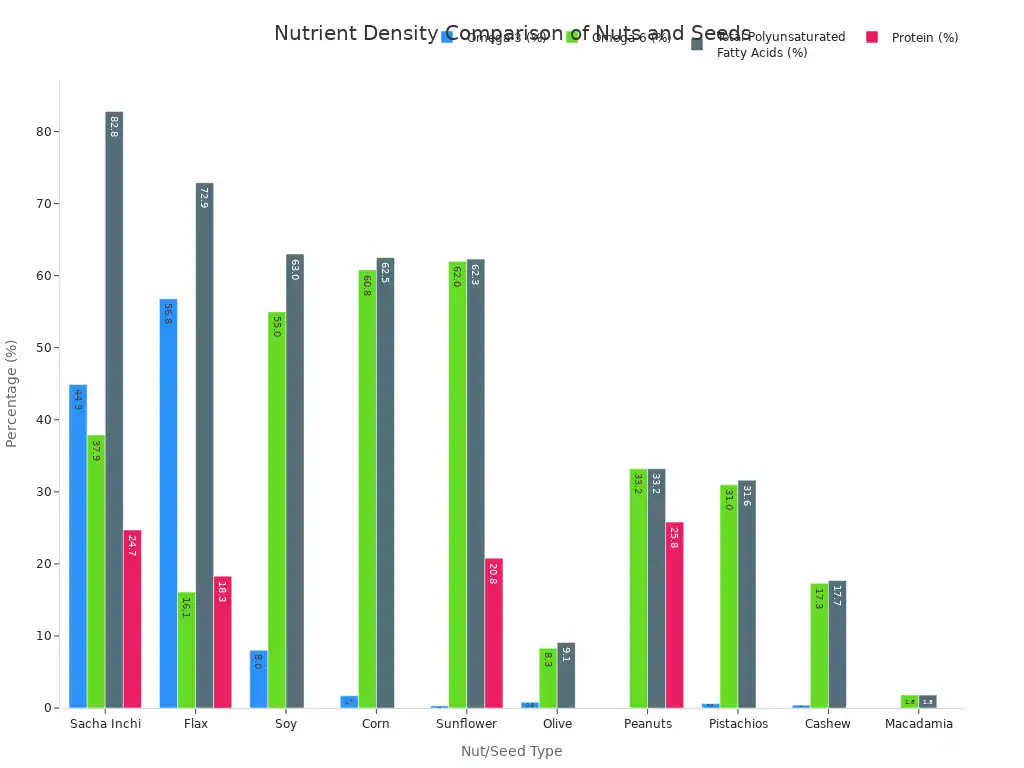
Sacha inchi stands out for its nutrient density. It offers more essential fats and protein than many other common nuts and seeds.
Nutrient Category | Sacha Inchi | Flax | Soy | Corn | Sunflower | Olive | Peanuts | Pistachios | Cashew | Macadamia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Omega-3 (%) | 44.9 / 40.6 | 56.8 | 8.0 | 1.7 | 0.3 / 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
Omega-6 (%) | 37.9 / 43.6 | 16.1 | 55.0 | 60.8 | 62.0 / 68.9 | 8.3 | 33.2 | 31.0 | 17.3 | 1.8 |
Total Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (%) | 82.8 / 84.5 | 72.9 | 63.0 | 62.5 | 62.3 / 69.0 | 9.1 | 33.2 | 31.6 | 17.7 | 1.8 |
Protein (%) | 24.7 | 18.3 | N/A | N/A | 20.8 | 0.0 | 25.8 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Sacha inchi seeds have high omega-3 and other essential fatty acids. They also contain much protein. They show a higher percentage of total polyunsaturated fatty acids than flax, soy, corn, sunflower, and olive oil. Values are 82.8% and 84.5% in different tests. Sacha inchi contains 44.9% or 40.6% omega-3. It has 37.9% or 43.6% omega-6. For protein, sacha inchi seeds contain 24.7%. This is similar to peanuts (25.8%). It is more than sunflower seeds (20.8%), flax seeds (18.3%), and sesame seeds (17.3%).
Unique Nutritional Composition
Sacha inchi has a unique nutritional makeup. It is a complete protein. It contains all essential amino acids. This is rare among plant proteins. Its protein digestibility is very high. Over 96% of the protein in its seeds is digestible. This is uncommon for plant-based protein sources. Healthy fat content helps protein absorption.
Sacha inchi oil has much omega-3 fatty acids. These make up almost 50% of its content. This makes it a unique plant source. It also has omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids. This profile makes it a good choice for neurocognitive health. It is a beneficial alternative to cod liver oil. It fits nutritional advice for omega-3 intake.
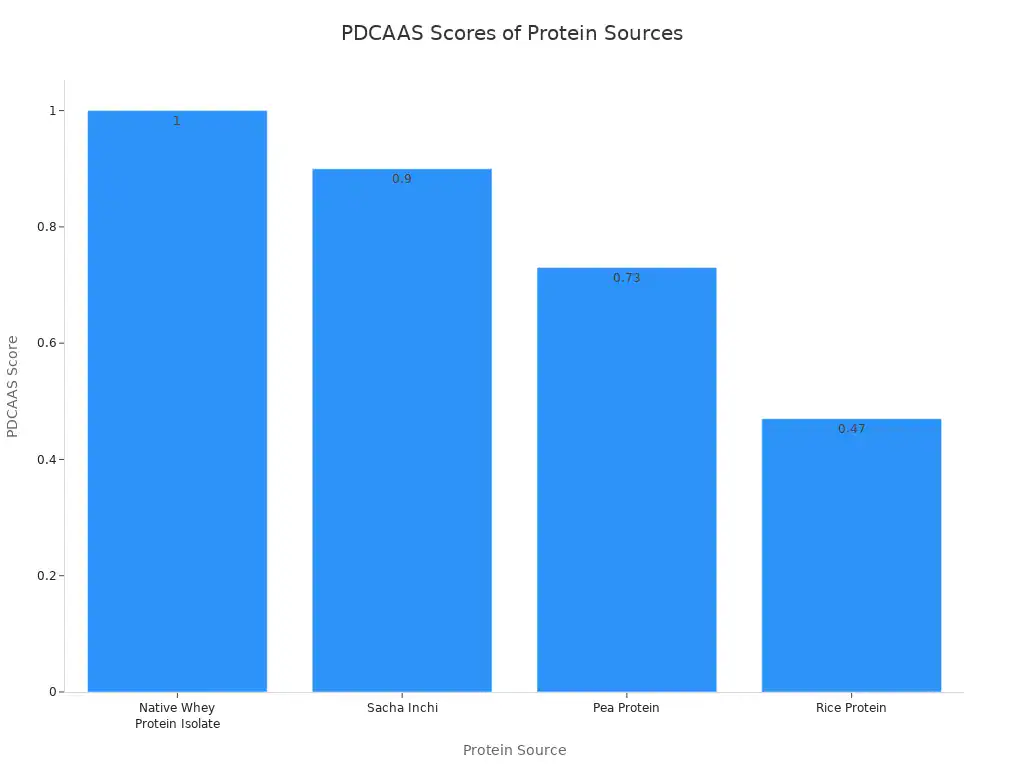
Sacha inchi powder is a superfood. It has 60% protein. It also has all 20 amino acids, including 9 essential ones.
Protein Source | PDCAAS Score |
|---|---|
Native Whey Protein Isolate | 1 |
Sacha Inchi | 0.9 |
Pea Protein | 0.73 |
Rice Protein | 0.47 |
Other unique compounds include:
High content of Omega 3 (around 50% of fat) with a balanced proportion of Omega 6.
Excellent source of vitamins A and E.
Rich in minerals such as calcium, zinc, and potassium.
Contains fiber.
Uniquely high Tryptophan content, which is crucial for mood, sleep, and hunger regulation.
Sustainable Sourcing
Sacha inchi cultivation supports sustainable practices. Farmers can grow it on degraded soils. It needs few agrochemical inputs. These methods help biodiversity. They also reduce environmental harm.
Growing sacha inchi helps soil conservation. It aids in preserving biodiversity. It also helps carbon sequestration. Organic certification is important. Most production is now organic. There is a chance to grow certified sustainable and fair trade practices. Blockchain technology can show supply chain details. Cultivation needs minimal pesticides and fertilizers. This fits eco-friendly production. Products should have organic, non-GMO, and fair trade labels. Vendors should show clear sourcing and traceability. This ensures sustainability.
Using Sacha Inchi
People can incorporate sacha inchi into their diets in various forms. Historically, the Incan people consumed sacha inchi seeds as food. They also extracted nutrient-rich oil from them. These sacha inchi seeds are a rich plant-based source of essential fatty acids and vitamins.
Seeds: Raw or Roasted
You can enjoy sacha inchi seeds raw or roasted. After harvest, workers place sacha inchi capsules in a ventilated oven. They dry them at 35 °C for three hours. This process partially opens the lobes. Then, they carefully unshell and uncoat the seeds to maintain their integrity. For roasting, they prepare the unshelled seeds. Roasting occurs for 15 minutes in a non-ventilated laboratory oven. Temperatures range from 80 °C to 160 °C. After roasting, the seeds cool to room temperature. People can then finely grind the seeds and store them. Alternatively, they peel the sacha inchi seeds. Then, they grind the shelled seeds using a milling machine. The ground seed kernels are sieved to a specific size. Finally, they vacuum-pack the prepared seeds and store them in a refrigerator.
Sacha Inchi Oil
Sacha inchi oil is a versatile product. Its kernels contain 35-60% lipids, 25-30% proteins, vitamin E, and polyphenols. The oil is rich in bio-available antioxidants. These include carotenes, phytosterols, and tocopherols. These compounds protect against oxidative stress. The oil can improve lipid profiles. It reduces total and LDL cholesterol. It also increases HDL cholesterol. It improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity. This makes it beneficial for cardiometabolic health.
Sacha Inchi Powder
Sacha inchi powder comes from cold-pressed and defatted seeds. This process retains all natural nutrients. While some use the powder in external applications like moisturizers, soaps, and cosmetics, it also has culinary uses.
Recipe Integration
Sacha inchi powder integrates easily into many recipes. You can add it to smoothies for a protein-packed drink. Mix it into yogurt or oatmeal for added protein and healthy fats. Use it in homemade protein bars, energy balls, or granola. It also works in baking as a flour substitute. It adds a nutty flavor and protein. Specific recipes include Peanut Butter Oatmeal Cookies with sacha inchi powder. You can also make Tomato Zucchini Focaccia with sacha inchi powder.
Side Effects and Precautions
While sacha inchi offers many benefits, people should know about potential side effects and precautions. Understanding these helps ensure safe consumption.
Digestive Sensitivity
Some individuals report digestive issues when they first consume sacha inchi. Nausea is the most frequently reported side effect. This feeling often lessens as the body adjusts to regular consumption. Starting with small amounts can help the digestive system adapt.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to sacha inchi are uncommon. However, some people have reported them. As with any new food, individuals with known allergies to nuts or seeds should exercise caution. They should consult a doctor before adding sacha inchi to their diet.
Recommended Intake
Raw sacha inchi seeds contain dangerous phytotoxins. They also have compounds that can impede nutrient absorption. These raw seeds can be harmful, even lethal in large quantities. Therefore, people should never consume raw sacha inchi seeds. Roasting or heating destroys these toxins and significantly reduces antinutrients. Always choose processed sacha inchi seeds or oil.
Sacha inchi contains a high amount of tryptophan. This amino acid can interact with mood-altering medications. People taking such medications should consult their healthcare provider. This ensures their continued health and avoids potential interactions.
Sacha inchi nuts offer a nutritional powerhouse. They provide essential Omega-3s, high protein, and many superfood qualities. Sacha inchi is versatile. People easily incorporate its seeds into various diets. These beneficial seeds offer a natural boost in health and wellness. This ancient superfood gains growing recognition in modern nutrition for its significant health benefits.
FAQ
What are Sacha Inchi nuts?
Sacha Inchi nuts are seeds from the Plukenetia volubilis plant. This plant grows in the Amazon rainforest. People also call them “Inca peanuts” or “Inca nut seeds.” They are an ancient superfood.
What key nutrients do Sacha Inchi nuts contain?
Sacha Inchi nuts offer high levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. They also provide complete plant-based protein. These nuts contain vitamins E and A, along with minerals like iron, magnesium, and calcium.
What forms of Sacha Inchi can people consume?
People can eat Sacha Inchi as roasted seeds. They also use its oil in cooking or as a dietary supplement. Sacha Inchi powder adds nutrients to smoothies, yogurts, and baked goods.
What makes Sacha Inchi a superfood?
Sacha Inchi earns its superfood status from its exceptional nutrient density. It has a unique composition of complete protein and high Omega-3 fatty acids. Its sustainable cultivation practices also contribute to this recognition.




