
You might wonder why The Sun and Your Health are closely linked. Your body relies on sunlight to produce vitamin D, which you cannot get directly from other vitamins through sun exposure. Many people do not get enough vitamin D. The following is some research I came across regarding this.
Vitamin D Level (nmol/L) | Percentage of Population (%) |
|---|---|
Less than 30 | 15.7 |
Less than 50 | 47.9 |
Less than 75 | 76.6 |
Sunlight helps your skin make vitamin D more effectively than most foods or supplements. You can learn why understanding this process is important for your health and how to get vitamin D safely.
Sunlight triggers vitamin D production in your skin.
Dietary sources and supplements help, but sunlight is often more effective.
The Sun and Your Health
Why Sunlight Matters
You might wonder why the sun and your health are so closely connected. The sun does much more than just help your body make vitamin d. When you spend time in the sun, your body reacts in many helpful ways.
The sun helps your skin release nitric oxide, which can lower your blood pressure and improve your heart health.
Sunlight boosts the production of serotonin and beta-endorphins. These chemicals help you feel happier and more relaxed.
The sun helps set your body’s internal clock, called the circadian rhythm. This rhythm controls your sleep and wake cycles, which are important for your overall health.
Sunlight can even help your immune system work better.
You also get other health benefits from safe sun exposure. Studies show that people who get enough sunlight may have lower rates of certain tumors. The sun can help your body fight inflammation, which may slow down some diseases. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can change how your immune cells work, which may affect autoimmune diseases.
Regular time in the sun can help your brain, too. Sunlight supports better memory and learning. It also helps lower your risk of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke by raising your vitamin d levels.
The Link to Vitamin D
The sun and your health are linked most strongly through vitamin d. Your skin uses the sun’s ultraviolet light to make this important vitamin. Scientists have found that sunlight is the main way your body increases its vitamin d levels.
This process depends on where you live, the season, and your skin color. Children who live in sunny places usually have enough vitamin d, but those in colder, darker areas may not. When you get the right amount of sun, your body makes enough vitamin d to support strong bones, a healthy immune system, and lower cancer risk. The sun and your health go hand in hand because of this special connection.
Vitamin D Production
The Science Behind the Sunshine Vitamin
You might wonder why your body needs the sun to make vitamin D. The answer lies in a special process that starts in your skin. When you step outside, sunlight touches your skin and sets off a chain reaction. This reaction helps your body create the sunshine vitamin, which is vital for your health.
Sunlight exposure is the main source of vitamin D for most people.
The sun gives off ultraviolet-B (UVB) rays. These rays have wavelengths between 290 and 315 nanometers.
Your skin contains a substance called 7-dehydrocholesterol. When UVB rays hit your skin, 7-dehydrocholesterol absorbs the energy.
This absorption happens mostly in the outer layers of your skin, called the epidermis, especially in cells named keratinocytes.
The energy from UVB changes 7-dehydrocholesterol into previtamin D3.
Previtamin D3 then changes shape to become vitamin D3, also called cholecalciferol.
Vitamin D3 enters your bloodstream with the help of a special binding protein.
Tip: The process works best when the sun is high in the sky, usually around midday.
Vitamin D synthesis is most efficient when your skin receives UVB light in the 290–300 nm range. Scientists have found that light at 293 nm works even better than regular sunlight. This means your body makes vitamin D faster and more easily when the sun’s rays are strong and direct.
You might ask why 7-dehydrocholesterol is so important. This substance acts like a sponge, soaking up UVB rays and starting the vitamin D production process. Your skin usually has enough 7-dehydrocholesterol to meet your needs, as long as you get enough sun.
The journey of vitamin D does not end in your skin. After your skin makes vitamin D3, your liver and kidneys help turn it into its active form. This active form acts more like a hormone than a regular vitamin. It travels through your body and helps control many important functions, such as bone health, immune defense, and even your mood.
Note: Vitamin D stands out because it acts as both a vitamin and a hormone. It helps your body balance calcium and phosphorus, supports your heart, and boosts your immune system. Low levels of vitamin D can affect your thinking skills and increase your risk of infections.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Synthesis
You may wonder why some people need more sun to make enough vitamin D. Several factors change how well your skin can produce this sunshine vitamin.
Factor | Effect on Vitamin D Synthesis |
|---|---|
Skin Pigmentation | Increased melanin in darker skin reduces UVB penetration, requiring longer sun exposure. |
Age | Older adults have reduced capacity for vitamin D synthesis, decreasing by about 13% per decade. |
Latitude and Season | Higher latitudes and winter months reduce UVB intensity, making synthesis minimal or absent. |
If you have darker skin, your body needs more time in the sun to make the same amount of vitamin D as someone with lighter skin. Melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, blocks some UVB rays.
As you get older, your skin makes less vitamin D. The ability drops by about 13% every ten years.
Where you live matters. People who live farther from the equator or in places with long winters get less UVB. This makes vitamin D production harder during certain months.
You might also wonder about sunscreen. Many people think sunscreen blocks all vitamin D production, but this is not true.
Sunscreen protects your skin from sunburn but still lets some UVB rays reach your skin.
Studies show that regular sunscreen use does not usually cause vitamin D deficiency.
You can still improve your vitamin D levels while protecting your skin.
Tip: If you worry about your vitamin D levels, talk to your healthcare provider. They can check your levels and suggest ways to get enough vitamin D.
Vitamin D is unique. Your body can make it with help from the sun, and it acts like a hormone to keep you healthy. Understanding why and how your skin makes vitamin D helps you make better choices for your health.
Health Benefits of Vitamin D
Strong Bones and Teeth
You need vitamin D to keep your bones and teeth strong. When you get enough sun, your skin makes this vitamin, which helps your body absorb calcium. Without enough vitamin D, your bones can become weak and break easily.
Okay, you can ask me ” Why this happens ?”
Mainly, this happens because vitamin D controls how your body uses calcium and phosphorus. If your vitamin D levels drop, your body cannot build or repair bone as well. Severe lack of this vitamin can cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. These conditions make bones soft and weak.
Vitamin D also helps your muscles work better. Strong muscles lower your risk of falling, which means fewer broken bones. Studies show that people with higher vitamin D levels have better bone mineral density. This means their bones are less likely to break. The table below shows how vitamin D levels affect bone health:
Vitamin D Level | Serum β-CTX Increase (%) | TRAP5b Increase (%) | Serum Calcium Decrease (%) | Calcium-Phosphorus Product Decrease (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥ 75 nmol/L | 224% | 22.2% | -1.3% | -2.6% |
< 75 nmol/L | 146% | 9.1% | -1.9% | -3.3% |
Low vitamin D levels also raise your risk of fractures. The chart below shows how fracture risk increases as vitamin D drops:
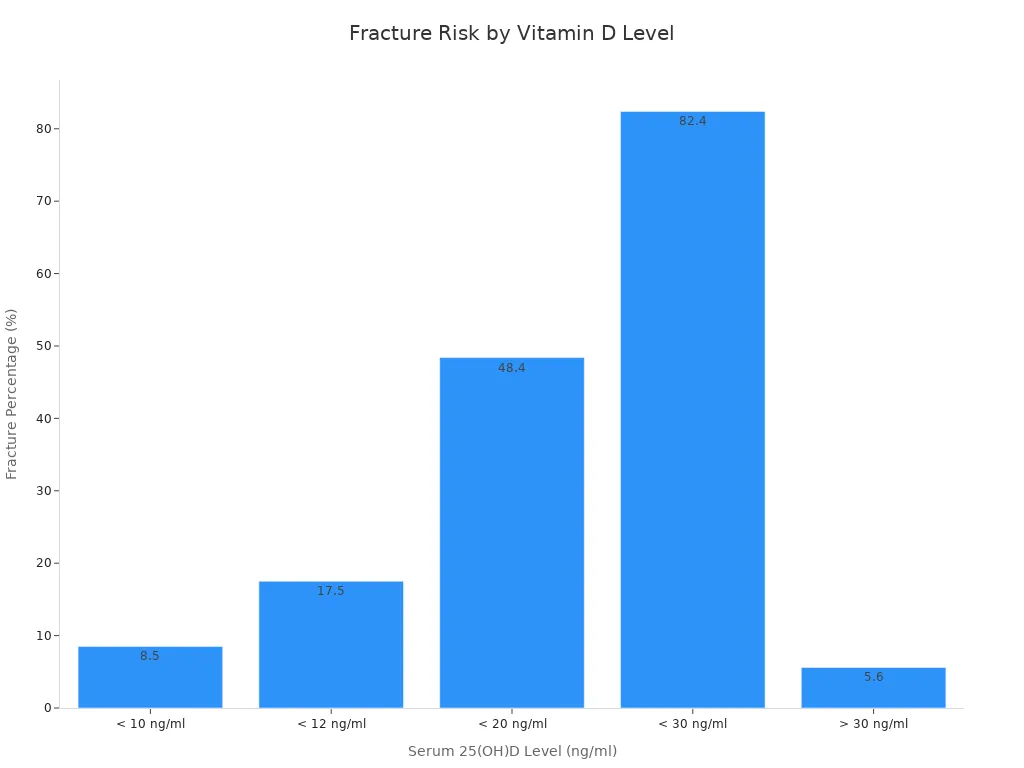
Immune and Blood Cell Support
You might wonder why vitamin D is important for your healthy immune system. This vitamin helps your body fight off germs and infections. Almost every immune cell has vitamin D receptors. When you get enough sun, your body makes more vitamin D, which helps control how your immune cells work. This means you have enhanced immunity and a lower risk of getting sick.
Vitamin D also helps your body make blood cells. It supports the growth and function of cells like monocytes, macrophages, and B cells. These cells protect you from disease and help your body heal. When your vitamin D levels are low, your body cannot make these cells as well, which can weaken your immunity.
Vitamin D helps regulate immune cell activity.
It supports the production of blood cells needed for fighting infections.
It helps control inflammation, which protects you from diseases like cancer.
Mood and Well-Being
Vitamin D does more than protect your body. It also helps your mind. You need enough vitamin D to feel your best. Low vitamin D levels link to a higher risk of depression and mood problems. Your brain has vitamin D receptors, which help control chemicals like serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals affect your mood, sleep, and how you handle stress.
Studies show that people with low vitamin D often feel sad or tired. When you get enough sun, your body makes more vitamin D, which can help you feel happier and more relaxed. This vitamin also protects your brain from inflammation and helps your nerves work well. Keeping your vitamin D levels up supports your mental health and may lower your risk of cancer.
Safe Sun Exposure for Vitamin D

How Much Sun Do You Need?
You might wonder why getting the right amount of sun is important for vitamin d. Your body needs sunlight exposure to make sufficient vitamin d for optimal health. The amount of sun you need depends on your skin color, age, where you live, and the season. Research shows that latitude affects how much UVB light reaches your skin, especially in winter. People living farther from the equator need more sunlight exposure to get enough vitamin d. Sun exposure works best around midday, when UVB rays are strongest. At other times, you need longer exposure to make the same amount of vitamin d.
Most people need between 5 to 30 minutes of daily sunlight exposure on their face, arms, and legs.
Lighter skin makes vitamin d faster, so you may need less time in the sun.
Darker skin has more melanin, which blocks UVB rays. You need more sun to make sufficient vitamin d.
Older adults produce less vitamin d from sunlight, so they may need extra time or a daily supplement.
Tip: Limit unprotected sun exposure to no more than 30 minutes to lower your risk of skin damage.
Protecting Your Skin
You need to balance making vitamin d with protecting your skin from harm. Too much sun can cause sunburn, photoaging, and even skin cancer. UVA rays damage all layers of your skin, leading to wrinkles and loss of tone. UVB rays cause sunburn and can damage DNA, raising your risk of skin cancer.
Use sunscreen with a high UVA protection factor to prevent sunburn while still allowing vitamin d synthesis.
Sunscreens with SPF 15 can help you get sufficient vitamin d and protect your skin.
Wear hats and sunglasses for extra protection during long periods outdoors.
Note: High UVA-PF sunscreens let more UVB through, which helps your body make vitamin d.
Special Considerations
Some people need to think more about how they get vitamin d. If you have darker skin or are over 70, your body makes less vitamin d from sunlight. You may need more time outside or consider vitamin d supplements. If you live in a place with little sunlight, especially in winter, you might not get enough vitamin d from the sun alone. The recommended dietary allowance for vitamin d is 600 IU per day for most people and 800 IU for those over 70, especially if you have limited sun exposure.
People with darker skin need more sun to make sufficient vitamin d.
Older adults may need a daily supplement to reach healthy vitamin d levels.
Supplements can help if you cannot get enough vitamin d from sunlight exposure.
Getting the right amount of sun helps your body make sufficient vitamin d, but you should always protect your skin to stay healthy.
Can the Sun Provide Other Vitamins?
Myths vs. Facts
You may hear people say that sunlight gives you many vitamins. This idea is a myth. The sun helps your body make vitamin D, but it does not provide other vitamins directly. Your skin cannot make vitamin C, vitamin A, or B vitamins from sunlight. You must get these nutrients from food. Some people think more sun exposure will fix any deficiency, but this is not true. If you have a deficiency in other vitamins, sunlight will not solve the problem.
Many people worry about vitamin d deficiency because it is common. You might notice signs of vitamin d deficiency, such as weak bones or feeling tired. Sun exposure helps your body avoid this deficiency, but it does not help with other vitamin deficiencies. You need a balanced diet to get all the vitamins your body needs.
The Sun’s Indirect Role
You may wonder why sunlight still matters for your health beyond vitamin D. Sun exposure supports your body in other ways, even if it does not give you more vitamins directly. When you spend time in the sun, your body starts important processes that help you use nutrients better.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Hormone Production | Sunlight exposure increases the expression of the POMC gene, leading to hormones that can influence nutrient absorption and overall health. |
Nitric Oxide Release | Sunlight exposure promotes the release of nitric oxide, which helps blood flow and nutrient delivery. |
Wound Healing | Sunlight exposure can help your skin heal, which may improve nutrient absorption by keeping your skin healthy. |
Sunlight also helps set your body’s internal clock. This clock, called your circadian rhythm, controls how your body uses energy and nutrients. Here are some ways sunlight affects your metabolism:
Sunlight acts as an energy source for your body’s processes.
Special cells in your eyes detect light and help set your circadian rhythm.
Disrupted light cycles can harm your metabolism and sleep.
Sunlight exposure can change how your body handles food and sugar.
You need sun exposure to avoid vitamin d deficiency, but you also need it for healthy metabolism. If you do not get enough sun, you may face a higher risk of deficiency and poor nutrient use. Remember, sun exposure is important, but it cannot replace a healthy diet.
Vitamin D is the main vitamin your body makes with help from the sun. You need this vitamin for strong bones, a healthy immune system, and better mood. Safe sun habits matter because too much sun can harm your skin, but too little may lead to deficiency. Your age, skin tone, and lifestyle change how much sun you need. If you have darker skin or live far from the equator, you may need more sunlight or a supplement. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about your vitamin D levels.




